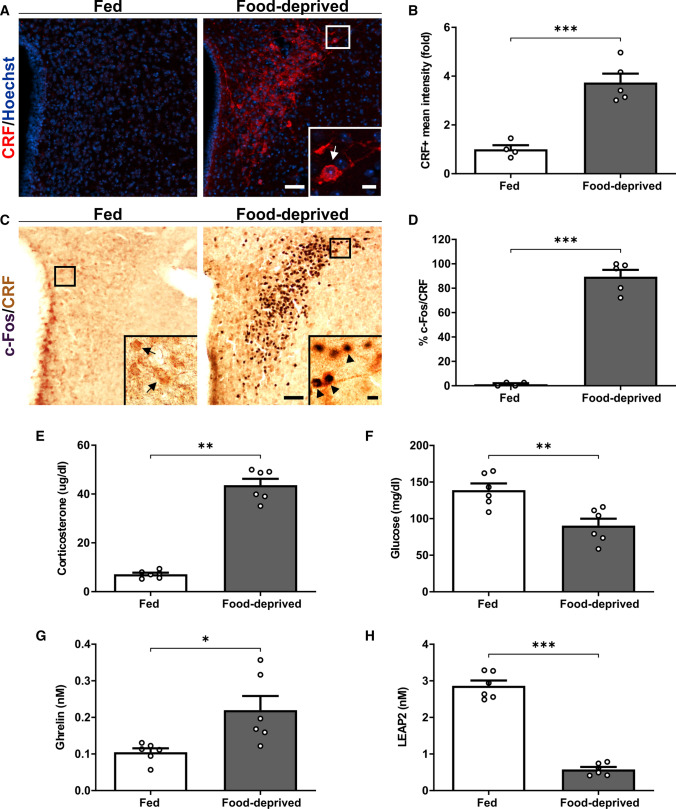
Fig. 1.
Food deprivation-induced activation of PVHCRF neurons is associated with an increase of ghrelin and a decrease of LEAP2 levels in plasma. A Representative photomicrographs of the PVH in coronal brain sections of fed and food-deprived WT mice subjected to immunofluorescence against CRF (red). Cell nuclei were labeled with Hoechst (blue). Scale bars: 50 µm (low magnification) and 10 µm (high magnification). B Quantitative analysis of the mean intensity of the CRF + signal in the PVH of each experimental group. C Representative photomicrographs of the PVH in coronal brain sections of fed and food-deprived WT mice subjected to double IHC against c-Fos (black) and CRF (brown). Insets depict high magnification images of the areas marked in low magnification images. Arrows point to CRF + cells while arrowheads point to c-Fos + /CRF + cells. Scale bars: 50 µm (low magnification) and 10 µm (high magnification). D Percentage of CRF + cells positive for c-Fos in the PVH in each experimental condition. E Plasma corticosterone, F glucose, G ghrelin and H LEAP2 levels of mice in each experimental group. Bars indicate mean ± SEM. Circles represent individual values. P values for unpaired comparisons were calculated by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001