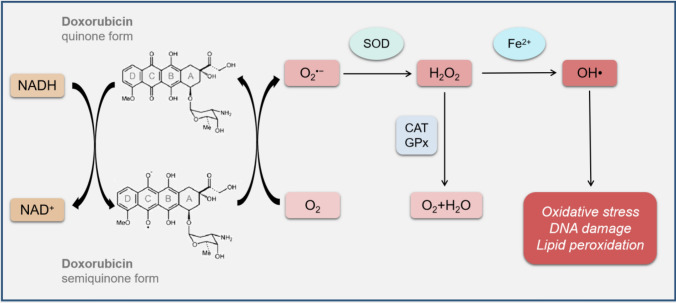
Fig. 1.
DOX-related redox cycling. The mitochondrial NADH-dependent enzymes can convert quinone moiety in ring C of DOX into semiquinone form through single-electron reduction. The semiquinone form of DOX reacts with O2 to form , which is neutralized by SOD to H2O2. In the presence of Fe2+, H2O2 might also generate highly reactive and toxic OH∙, which reacts with DNA, proteins and lipids, leading to DNA damage and lipid peroxidation. DOX doxorubicin, NADH nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydrate, O2 oxygen molecule, superoxide anion, SOD superoxide dismutase, H2O2 hydrogen peroxide, Fe2+ iron, OH∙, hydroxyl radical, CAT catalase, GPx glutathione-dependent peroxidase, H2O water