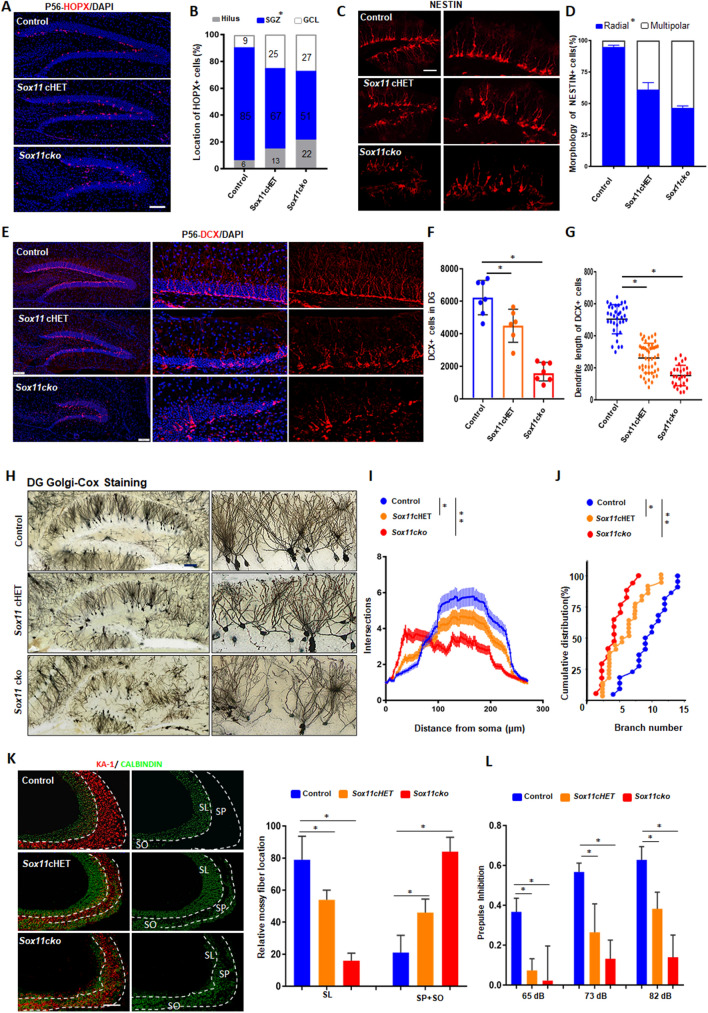
Fig. 2.
SOX11 deficiency results in random distribution and irregular morphology of hippocampal granule cells and causes diminished PPI. A Abnormal distribution of HOPX + NPCs in the DG in the SOX11-mutant adult brain. Scale bar, 100 μm. B Quantifications of HOPX + NPCs in the granule cell layer, SGZ, and hilus within the DG in adult mouse brain, n = 3 mice. Morphology (C) and quantification (D) of radial or multipolar NPCs in the DG in the SOX11-deficient or control mouse brain. Scale bar, 20 μm. Error bars, mean ± SEM, n = 5 mice. (Student’s t test). Distribution (E), quantification (F) and average dendrite length (G) of DCX + neuroblasts in the SOX11-deficient or control mouse hippocampus. Scale bar, 50 μm. Error bars, mean ± SEM (n = 7, *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA). H Golgi–Cox staining of the hippocampus (coronal section) from the SOX11-deficient or control mouse brain. Scale bar, 50 μm. I–J Sholl analyses of dendritic complexity of dentate granule cells in the SOX11-deficient or control mouse brain (I). Cumulative distribution of branch numbers of neurons in the DG granule cells in SOX11-deficient or control mouse brain. Error bars, mean ± SEM, n = 27, *p < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus the indicated group (Student’s t test). K Mossy fiber connections decreased to the SL region but increased to the SP and SO regions in the SOX11-deficient hippocampal CA3 region. Error bars, mean ± SEM, n = 3 mice, *p < 0.05, (one-way ANOVA). L PPI was diminished in the SOX11-deficient mice. Error bars, mean ± SEM, n = 13, *p < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA)