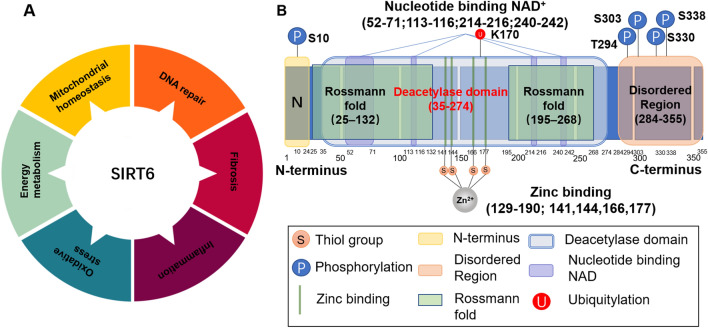
Fig. 1.
Structural features and biological functions of SIRT6. A Biological functions of SIRT6. SIRT6 can regulate telomere maintenance, DNA repair, energy metabolism, oxidative stress, the inflammatory response, and fibrosis to maintain cellular homeostasis. B Structural features of SIRT6. SIRT6 is composed of an N terminus (1–24), a C terminus (269–355), and a conserved central domain (25–274) and has a total length of 355 amino acids (aa). The conserved central domain is the main catalytic core, which includes the NAD+-binding Rossmann fold domain (RFD) (25–132 and 195–268) and a zinc-binding domain. Cysteine residues that bind to Zn2+ ions are located at positions 141, 144, 166, and 177. The C terminus is a disordered region that is proline-rich. The main phosphorylation and ubiquitylation sites are highlighted