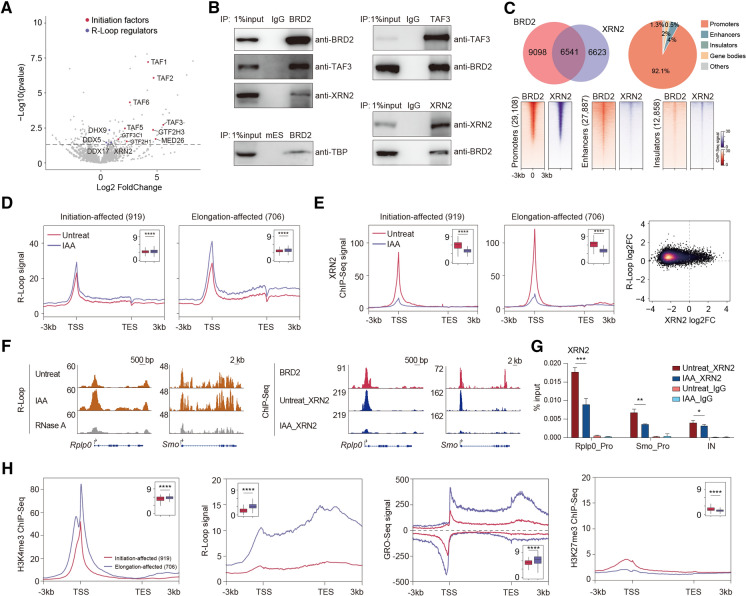
Fig. 2.
BRD2 depletion causes increased R-loop signals potentially underlying the roles of BRD2 in Pol II elongation. A Volcano plot displaying the enriched proteins identified by BRD2 ChIP-MS in mESCs. BRD2 ChIP-MS-enriched proteins were identified by DESeq2 using the PSM (peptide-spectrum match) values in BRD2 and input samples (2 repeats for each sample, p value < 0.05). The enriched initiation factors and R-loop regulators are shown in red and purple, respectively. B Western blot analyses of anti-BRD2, anti-TAF3 and anti-XRN2 immunoprecipitates in isolated chromatin fractions from wild-type mES cells show that BRD2 interacts with TAF3 and XRN2. Western blot analyses of anti-BRD2 immunoprecipitates in isolated chromatin fractions of BRD2 degron mES cells show that BRD2 interacts with TBP. C Pie chart (top left) showing the overlapping ChIP-Seq peaks between BRD2 and XRN2. The pie chart (top right) shows that the overlapping peaks of BRD2, and XRN2 ChIP-Seq occupy promoters. Heatmap plots (bottom) displaying the occupancy of BRD2 and XRN2 at promoters, enhancers, and insulators. D Meta-gene plots (left) of the average R-loop signals at initiation-affected and elongation-affected genes upon BRD2 depletion. Boxplots (insets) show log2 R-loop signals at ± 100 bp around TSSs upon BRD2 depletion. Significance was determined using the Wilcoxon test (****p < = 0.0001). Two replicates were done for each next-generation sequencing experiment. E Meta-gene plots (left) of the average XRN2 ChIP-Seq signals at initiation-affected and elongation-affected genes upon BRD2 degradation. Boxplots (insets) showing log2 XRN2 ChIP-Seq signals at ± 100 bp around TSS regions upon BRD2 depletion. Density scatter plots (right) showing the correlation of binding fold change between R-loop and XRN2 ChIP-Seq signals upon BRD2 depletion. Significance was determined using the Wilcoxon test (****p < = 0.0001). Two replicates were done for each next-generation sequencing experiment. F Left: genome browser track of S9.6 R-loop Cut&Tag signals in BRD2 degron mES cells under untreated and 3 h IAA-treated conditions at the Rplp0 and Smo loci. The RNase A-treated group served as a negative control. Right: genome browser track of XRN2 ChIP-Seq signals in BRD2 degron mES cells under untreated and 3 h IAA-treated conditions at the Rplp0 and Smo loci. G XRN2 ChIP-qPCR analyses of Rplp0 and Smo promoters and intergenic regions in BRD2 degron cells under untreated and 3 h IAA-treated conditions. The intergenic region serves as the negative control for ChIP-qPCR. Primers see Table S9. Error bars represent the SD of at least three technical replicates. p values were calculated using Student’s t test (*: p < = 0.05, **: p < = 0.01). H Meta-gene plots of the average H3K4me3, GRO-Seq, H3K27me3 ChIP-Seq and R-loop signals (public available dataset, see Table S8. The signal distribution is different from our R-loop signals in (D), as they were generated with different library preparation methods for R-loop sequencing) at initiation-affected and elongation-affected genes. Boxplots (insets) showing the log2 ChIP-Seq or GRO-Seq signals at ± 100 bp around TSS regions, or R-loop signals at gene body regions of initiation-affected and elongation-affected genes. Significance was determined using the Wilcoxon test (****p < = 0.0001)