Fig. 2.
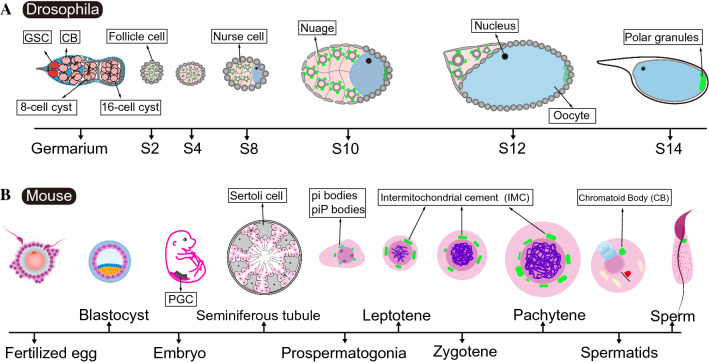
Schematic diagrams of germline development and dynamic distribution of nuage in Drosophila and mice. A Anatomy of the ovaries in a single ovariole illustrating nuage formation during Drosophila oogenesis. The Drosophila ovaries comprise 16–20 tubular structures, termed ovarioles, which are arranged as a production line-like assembly of differentiating egg chambers to produce mature eggs (oogenesis). The functional unit of the Drosophila ovary is termed the ovarian follicle, or egg chamber, originating from the germarium that is localized to the anterior tip in each ovariole. Germline stem cells (GSCs) (red) undergo asymmetric cell division, giving rise to one daughter stem cell that remains in contact with the Cap cells, and the other daughter cell destined to differentiate into Cystoblast (CB). Following four rounds of successively synchronous mitotic cell divisions, 16 interconnected cystocytes (light red) are produced, and subsequently bud off the germarium once they are surrounded by somatic follicle cells. During the development of each egg chamber, one of the 16 cystocytes is committed to meiosis and divides into the oocyte at the posterior end, whereas the remaining cells develop into polyploid nurse cells, which are interconnected through the intercellular bridges. Vasa-enriching nuage in nurse cells and Vasa-containing polar granules in oocyte are highlighted in green color. S, stage; B schematic diagram of nuage distribution (green color) in the male mouse germline. Primordial germ cells (PGCs) are induced in a subpopulation of the epiblast in the early embryos starting on embryonic day 6.5 (E6.5). Ddx4 is detectable in PGCs from E10 onwards. Pi-bodies and piP-bodies are present in prospermatogonia in the perinatal testis. Intermitochondrial cement (IMC) is present in the spermatocytes. The chromatoid body (CB) is assembled in haploid spermatids. All granules (green) are localized around the nuclear membrane within the cytoplasm