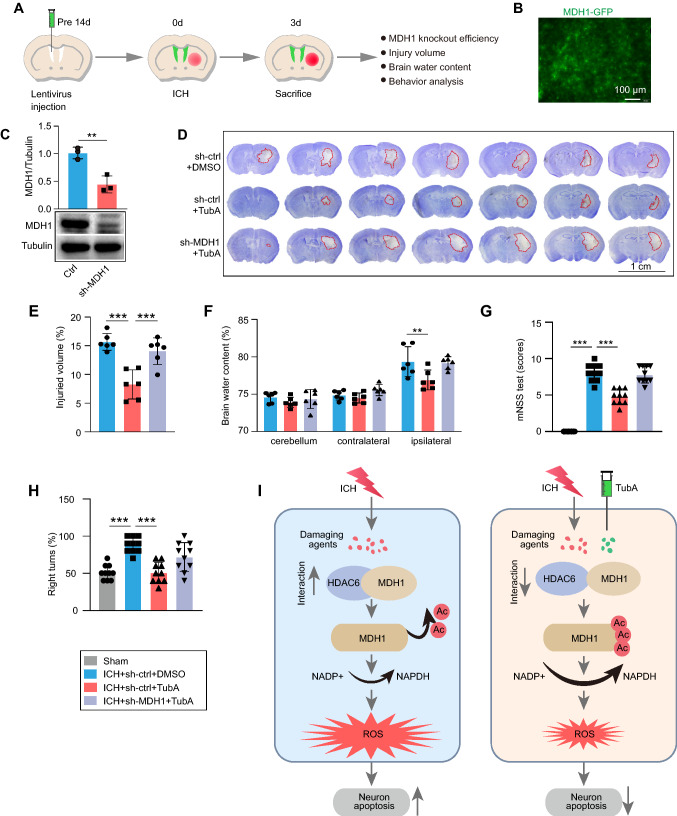
Fig. 7.
Protective effect of HDAC6 inhibition depends upon acetylation level of MDH1. A Experimental design for results presented in Fig. 7B–H. B–C Results of green-fluorescent protein (GFP)-MDH1 lentivirus in the brain were identified by B autofluorescence without primary antibody staining and C WB assay (n = 3/group). At day 3 following ICH, D–E brain injury was assayed by Nissl staining (n = 6/group), F cerebral edema was determined by the brain water content (n = 6/group), and G–H neurological function was assayed by mNSS score and corner-turning test (n = 10/group). I Model illustration of mechanism by which HDAC6/MDH1 signaling mediates oxidative stress-induced neuron apoptosis following ICH. Upon ICH injury, the interaction between HDAC6 and MDH1 was enhanced, which promoted HDAC6 mediated-MDH1 deacetylation at K121 and K298, thereby inhibiting NADP+ shift to NADPH; consequently, ROS was overproduced, which contributed to neuron apoptosis. However, administration of TubA (a specific HDAC6 inhibitor) alleviated the oxidative stress response by disrupting HDAC6 and MDH1 association, thus recovered neuron from apoptosis. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001