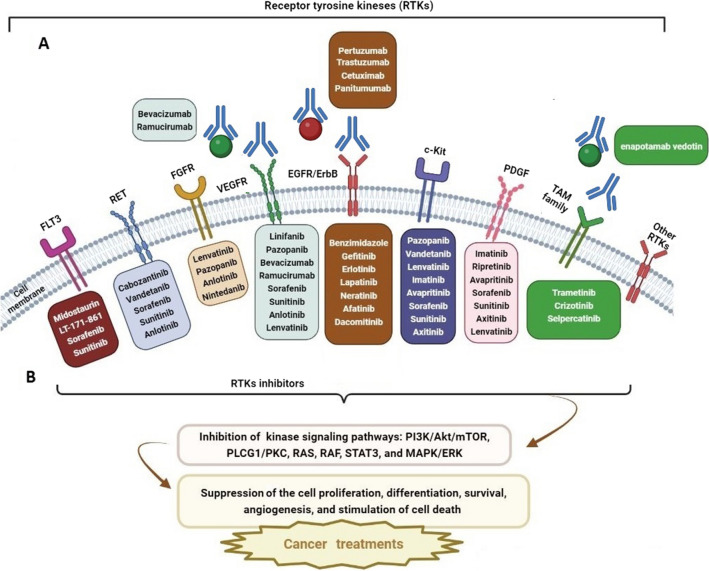
Fig. 2.
An overview of inhibition of cell cycle proliferation, differentiation, survival, angiogenesis, and also enhancement of cell death pathways by receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (RTKIs) that target tyrosine kinase receptors. Different kinase inhibitors in each box have been tested in different cancers and are listed according to the specificity and selectivity of the kinase receptor. A Monocolonal antibodies (mAbs) can target RTKs or ligands and inhibit RTK activation. B Small molecule inhibitors can target the ATP-binding site of RTKs in their interacellular domain and inhibit RTK phosphrylation. Therefore, the signaling cascade is blocked. FLT3 FMS-like tyrosine kinase-3; RET rearranged during transfection; FGFR fibroblast growth factor receptor; VEGFR vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; EGFR epidermal growth factor receptor; c-KIT Mast/Stem Cell Growth Factor Receptor Kit; PDGFR platelet-derived growth factor receptor; PI3K phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Akt V-Akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog; mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin; PLCG1/PKC phospholipase C gamma 1/protein kinase C; RAS rat sarcoma virus; RAF rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; STAT3 signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; MAPK/ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase