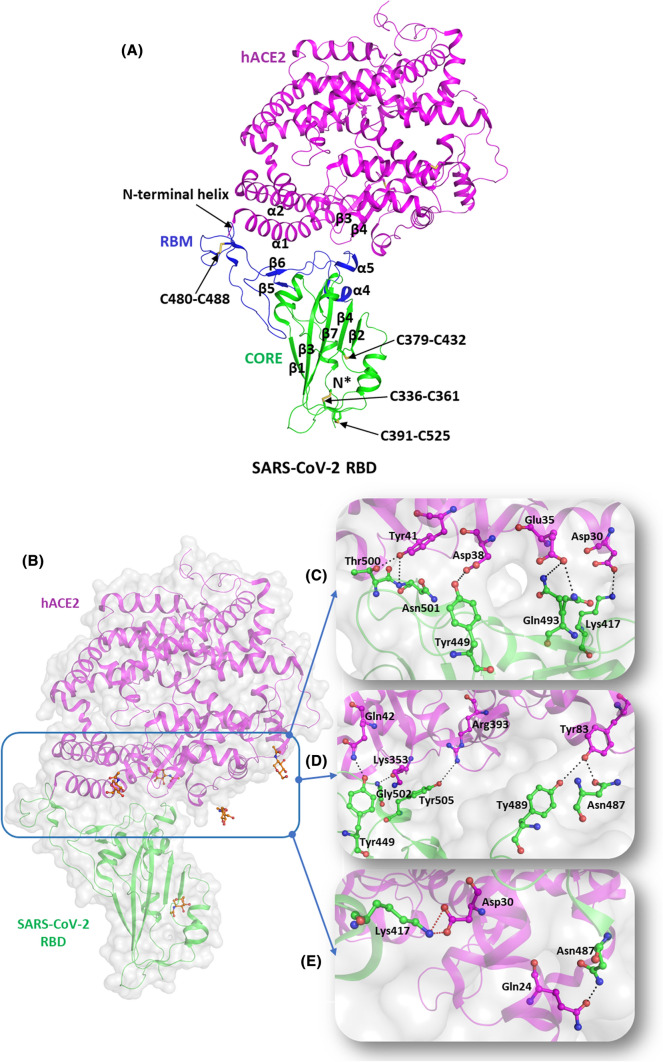
Fig. 3.
Molecular mechanisms of interaction of SARS-CoV-2 S protein with hACE2 receptors. (A) Structural representation of SARS-CoV-2 RBD (green, cartoon) with RBM (blue, cartoon) bound to hACE2 (magenta, cartoon) (PBD id: 6M0J). The disulfide bridges are highlighted in yellow (stick representation). (B) The interaction interface of hACE2 (magenta, cartoon) and SARS-CoV-2 (green, cartoon) with NAG (orange, ball and stick). Several hydrogen bonds interactions and salt bridges stabilize the RBD-hACE2 complex. (C) Hydrogen-bonded interactions involving residues Tyr449, Gln493, Thr500, and Asn501 of RBD (igreen, ball and stick) with Asp38, Glu35, and Tyr41 of hACE2 receptor, respectively. (D) Hydrogen-bonded interactions between the residues Tyr487 and Asn489 of RBD (green, ball and stick) and Tyr83 of hACE2 (magenta, ball and stick). It also depicts the involvement of Tyr449, Gly502, and Tyr505 residues of RBD (green, ball and stick) with Gln42, Lys353, and Arg393 of hACE2 (magenta, ball and stick) through H bonds. (E) Hydrogen-bonded interactions of Asp30 (RBD, green ball and stick) with Gln24 (hACE2, magenta, ball and stick) and salt bridge interactions between Lys 417 (RBD, green ball and stick) and Asp30 (hACE2, magenta, ball and stick). Hydrogen bonds are marked as blacked dotted lines and salt bridges as red dotted lines