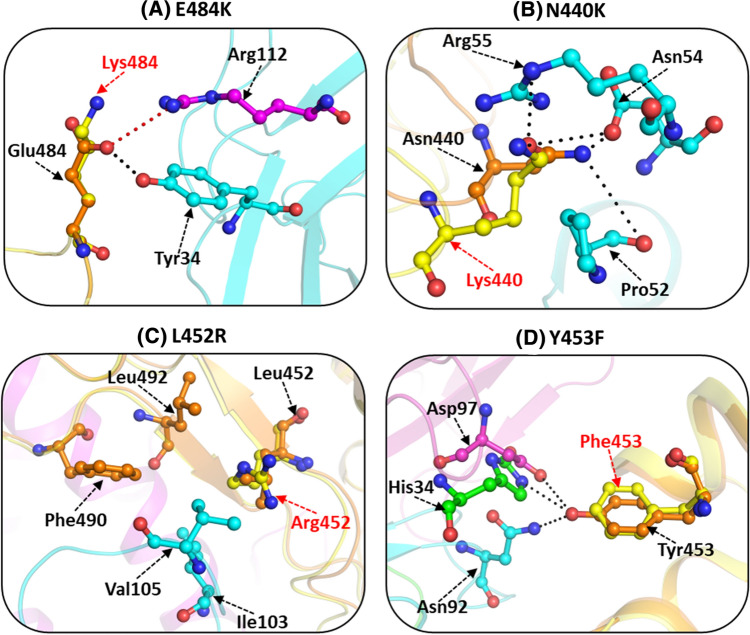
Fig.7.
Interactions of SARS-CoV-2 S protein mutants with neutralizing antibodies. Intermolecular non-covalent interactions of wild-type and mutant S protein with neutralizing antibodies, (A) N440K with antibody C135 (residues in cyan). S protein complex with Fab portion of C135 neutralizing antibody (PDB id: 7K8Z) was used as wild type while for mutant type PDB id: 6VXX was taken (B) L452R with REGN10933. RBD complex with REGN10933 neutralizing antibody (PDB id: 6XDG) was used as wild type while for mutant PDB id 6LZG was used (C) Y453F with CC12.1 (light chain and heavy chain residues are shown in cyan and magenta, respectively). RBD complex with CC12.1 neutralizing antibody (PDB id: 6XC2) was used as wild type while for creating mutant type PDB id: 6LZG was employed. (D) E484K with P2B-2F6 (light chain and heavy chain residues shown in cyan and magenta, respectively). RBD complex with P2B-2F6 neutralizing antibody (PDB id: 7BWJ) was utilized as wild type while for mutant (PDB id: 6LZG) was considered. Mutant structures were generated with PyMOL and were energy minimized. Wild-type S protein residues are shown in orange and mutated residues in yellow. Hydrogen bonds are marked as black dotted lines and salt bridges as red dotteded lines. Mutated residues are marked by red font