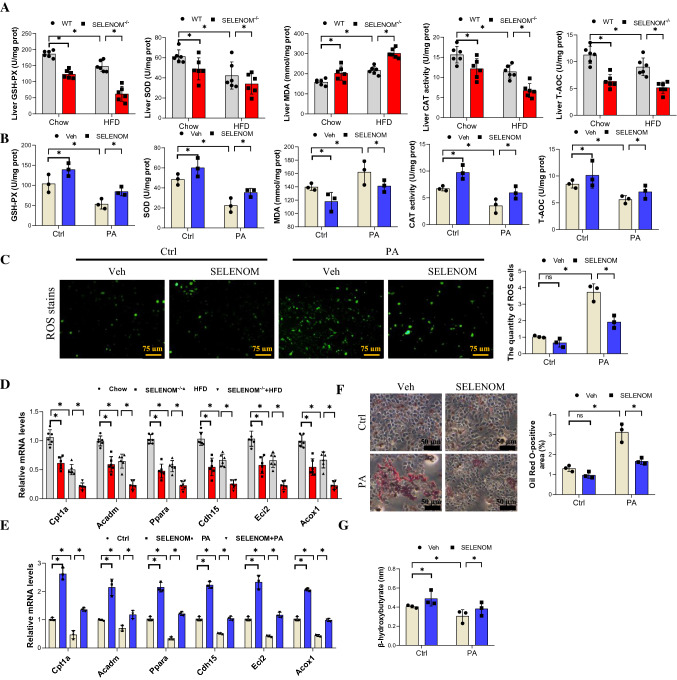
Fig. 4.
SELENOM−/− increases HFD-induced hepatic oxidative stress. A Oxidative stress markers of the GSH-PX, SOD, MDA, CAT, T-AOC contents were measured in the livers from WT, SELENOM−/−, HFD and SELENOM−/− + HFD (n = 6; *P < 0.05). B Oxidative stress markers of the GSH-PX, SOD, MDA, CAT, T-AOC contents were measured in hepatocytes of Veh, SELENOM, PA and SELENOM + PA (n = 3; *P < 0.05). Fields from one representative experiment of three are shown. C ROS staining was detected by immunofluorescence with DCFH-DA (green fluorescence, 5 mM) in hepatocytes of Veh, SELENOM, PA and SELENOM + PA (n = 3; *P < 0.05). D The mRNA levels of lipogenic genes such as Cpt1a, Acadm, Ppara, Cdh15, Eci2 and Acox1 in HFD-treated livers with SELENOM−/− (n = 6; *P < 0.05). E The mRNA levels of lipogenic genes such as Cpt1a, Acadm, Ppara, Cdh15, Eci2 and Acox1 in Veh, SELENOM, PA and SELENOM + PA (n = 3; *P < 0.05). F Oil Red O staining in hepatocytes of Veh, SELENOM, PA and SELENOM + PA. Ten fields (Scale bar: 50 μm) were randomly selected for each sample. The positive area in each image was measured (n = 3; *P < 0.05). G β-hydroxybutyrate contents were measured in the livers from WT, SELENOM−/−, HFD and SELENOM−/− + HFD (n = 6; *P < 0.05). Values represent means ± SEM