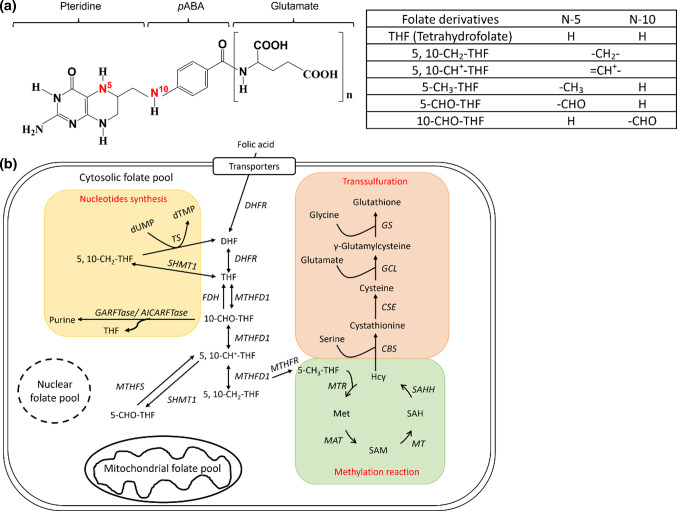
Fig. 1.
Folate and folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism. a Folate is composed of a pteridine ring and a p-aminobenzoic acid with 5–8 γ-linked glutamate residues attached to the carboxyl group of benzene ring. The one-carbon unit is attached to N5- and/or N10-position of pteridine ring at the oxidation levels of formate, formaldehyde and methanol. b The one-carbon units carried by reduced folate participate in the biosynthesis of purines, thymidylate, amino acid and S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) in cytosolic, mitochondrial and nuclear folate pools. The folate enzyme γ-glutamylhydrolase (γGH) converts polyglutamylfolates (folate-Glun) to monoglutamylfolates (folate-Glu1) and facilitate intracellular folate exportation, leading to intracellular folate deficiency (thickened circle and arrows in shadowed box). Enzyme abbreviations: DHFR dihydrofolate reductase, MTHFD methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase, FDH 10-formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase, GART glycinamide ribonucleotide transformylase, AICART aminoimidazolecarboxamide ribonucleotide transformylase, MTHFS 510-methenyltetrahydrofolate synthetase, SHMT Serine hydroxymethyltransferase, MTHFR methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, TS thymidylate synthase, MTR 5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase, MAT methionine adenosyl transferase, MT methyltransferase, SAHH S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase