Figure 1. Bacterial and fungal microbiota have a counteracting role in modulating immune responses induced by radiation therapy in the context of cancer.
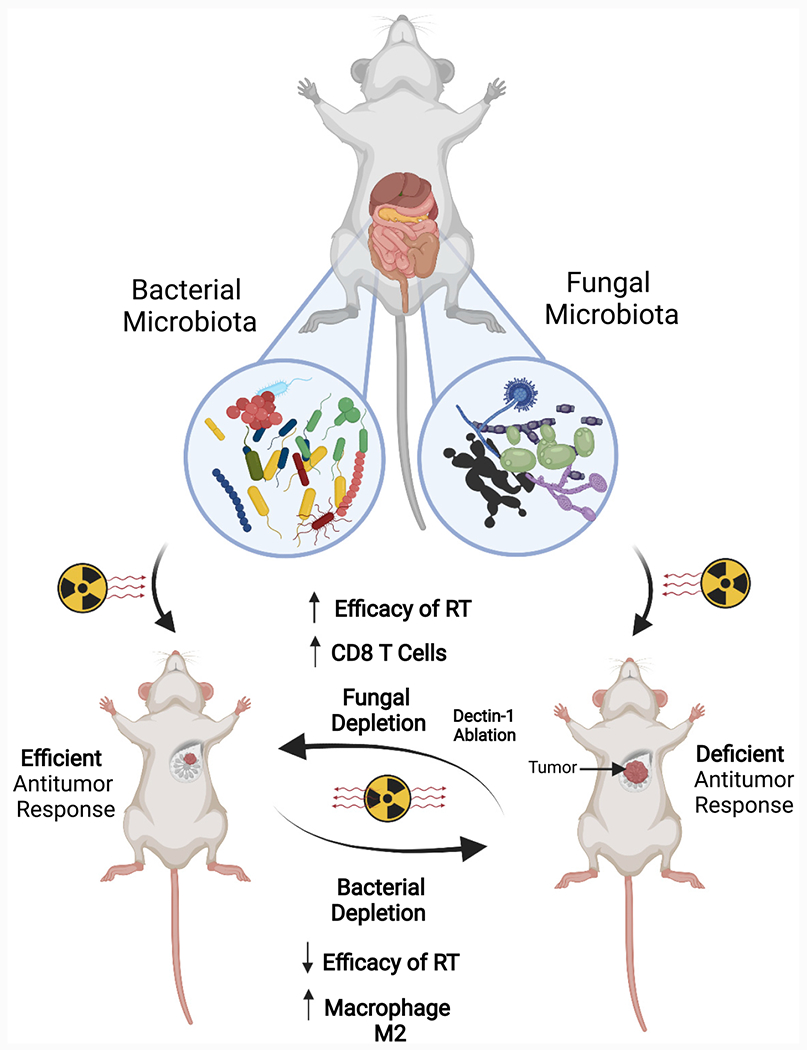
Bacterial ablation with antibiotics increases immune-suppressive populations and favors tumors’ growth while increasing fungal populations. In turn, antifungals increase cytotoxic immune T cell populations and delay tumor growth in response to radiation therapy.
