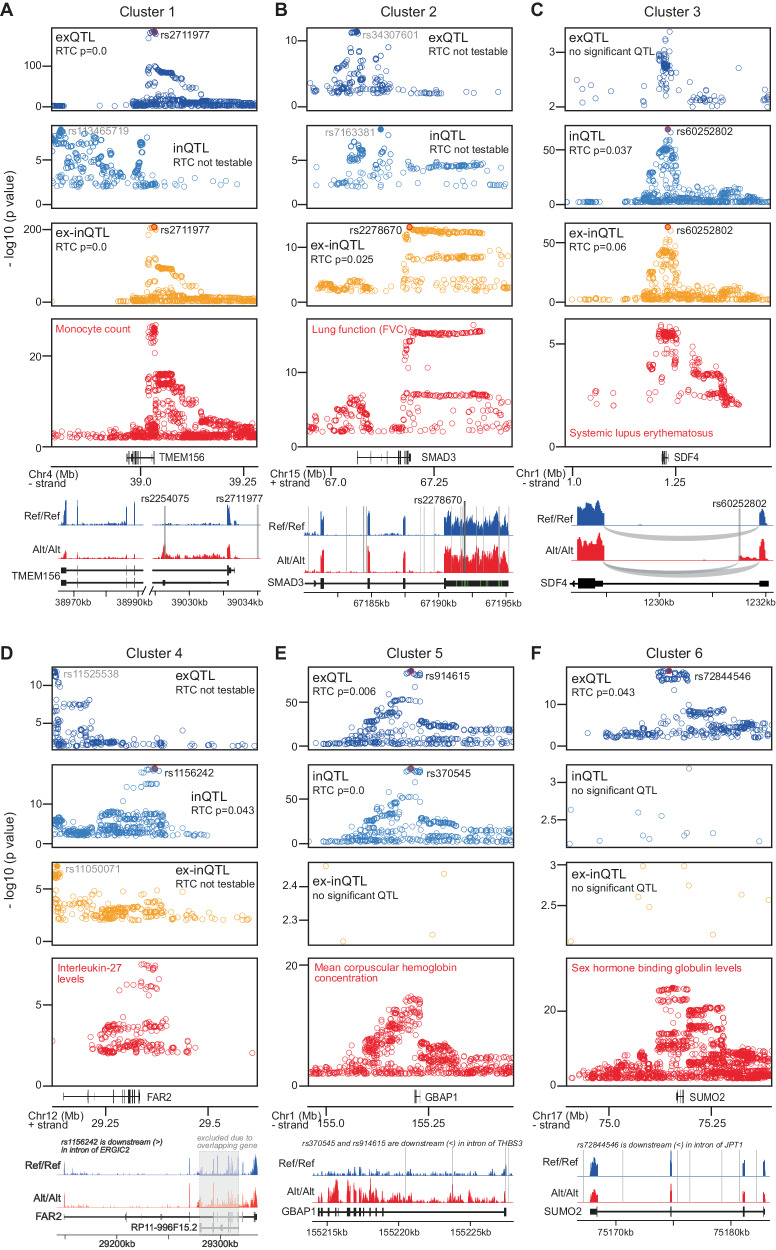
Fig. 5. Examples for cis-QTLs from different clusters colocalizing with GWAS variants.
In each subfigure, the top three panels show the -log10 nominal p-values (<0.01), in a region of 500 kb around the top cis-QTL (x-axis), for cis-QTL associations with exon levels (dark blue), intron levels (blue) and exon–intron-ratios (orange), and the fourth panel shows the −log10 p-values for the GWAS trait associations (red) in the same region. The rsID of the top cis-QTL(s) are indicated (in black, if colocalized with the GWAS trait variants, or in grey if not). The p value of the RTC (regulatory trait concordance) colocalization analysis is indicated inside each cis-QTL panel, in case colocalization was testable, i.e. QTLs and GWAS variants are within the same genomic region between recombination hotspots. The bottom panel shows examples for RNA-Seq read distributions at the associated gene from two homozygous individuals, one with reference (Ref/Ref; blue) and one with alternative (Alt/Alt; red) genotype, for the top cis-QTL variant. The positions of the top cis-QTL as well as QTLs sharing the cis-QTL signal are indicated with thick or thin lines, respectively. A A cis-QTL from cluster 1, associated with TMEM156 and colocalizing with a GWAS variant for monocyte count. B A cis-QTL from cluster 2, associated with SMAD3 and colocalizing with a GWAS variant for FVC, a trait related to lung function. C A cis-QTL from cluster 3, associated with SDF4 and colocalizing with a GWAS variant for systemic lupus erythematosus. D A cis-QTL from cluster 4, associated with FAR2 and colocalizing with a GWAS variant for interleukin-27 levels. E A cis-QTL from cluster 5, associated with GBAP1 and colocalizing with a GWAS variant for mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration. F A cis-QTL from cluster 6, associated with SUMO2 and colocalizing with a GWAS variant for sex hormone binding globulin levels.