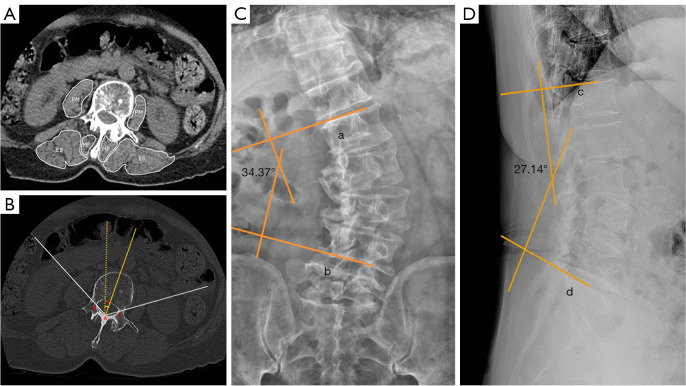
Figure 1.
Degenerative lumbar scoliosis radiography. (A) Delineation of paraspinal muscles in axial CT images. (B) Axical CT; Ho’s method. (A) is located at the junction of the inner surfaces of two laminae; (B) and (C) are situated at the corresponding junctions of the inner surfaces of the laminae and pedicles; the angle α between the bisector of the (BAC) angle and the sagittal plane is defined as the apical vertebral rotation angle; (C) standard anteroposterior radiography; line a is parallel to the upper endplate of the upper vertebra, while line b is parallel to the lower endplate of the lower vertebra; the angle between lines a and b is known as the Cobb angle; (D) standard lateral radiography; line c is parallel to the upper endplate of L1, while line d is parallel to the upper endplate of S1; the angle between lines c and d is known as the lumbar lordotic angle. PM, psoas major; MF, multifidus; ES, erector spinae; CT, computed tomography.