Figure 2. Strategies to enhance immunogenic cell death induced by RT.
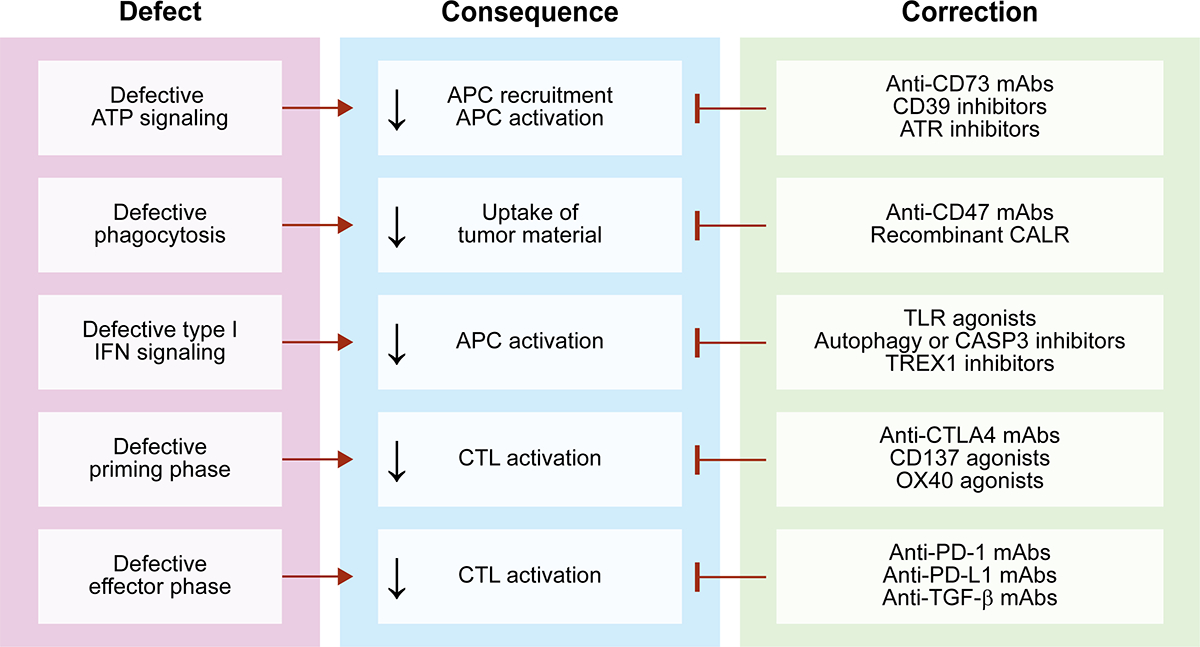
Depending on multiple variables, radiation therapy (RT) may kill cancer cells in the context of suboptimal immunostimulation, resulting in a variant of regulated cell death (RCD) with limited immunogenicity. A number of strategies have been investigated to circumvent these defects and restore superior immunogenic cell death (ICD)-driven adaptive immune responses against non-irradiated or radioresistant cancer cells. APC, antigen-presenting cell; ATR, ATR serine/threonine kinase; CD39 (official name: ENTPD1), ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1; CASP3, caspase 3; CD73 (official name: NT5E), 5’-nucleotidase ecto; CD137 (official name: TNFRSF9), tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 9; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; CTLA4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4; mAb, monoclonal antibody; OX40 (official name: TNFRSF4), tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 4; PD-1 (official name: PDCD1), programmed cell death 1, PD-L1 (official name: CD274); TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TREX1, three prime repair exonuclease 1.
