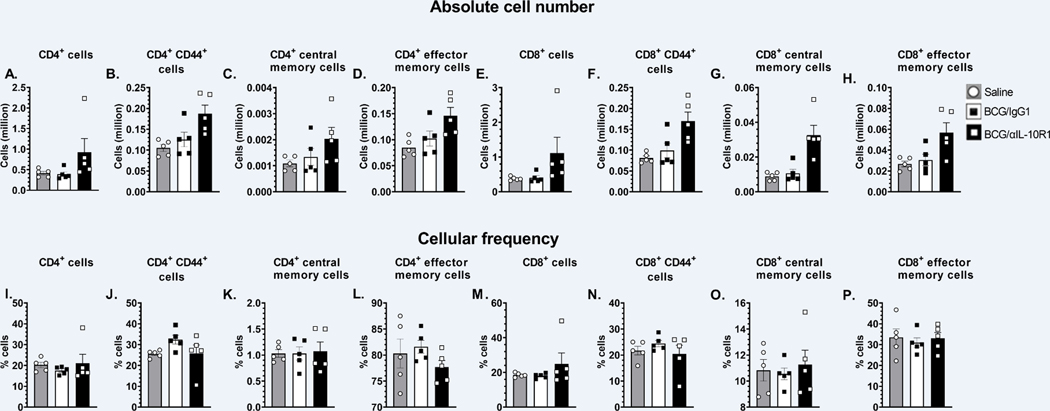
Figure 3. BCG/αIL-10R1 administration causes accumulation of central memory cells in lung.
WT mice were subcutaneously immunized with BCG/αIL-10R1 or BCG/IgG1. Immunized mice were euthanized at 7 weeks post immunization and lung mononuclear cells were harvested and stained with fluorescent dye tagged antibodies specific for CD4 and CD8 in combination with CD44, CD62L and CCR7 and acquired by flow cytometry and analyzed by FlowJo software. Absolute number and frequency of (A&I) CD4+, (B&J) CD4+ CD44hi (C&K) CD4+ CD44hi CD62L+ CCR7+ central memory, (D&L) CD4+ CD44hi CD62L− CCR7− effector memory, (E&M) CD8+, (F&N) CD8+ CD44hi, (G&O) CD8+ CD44hi CD62L+ CCR7+ central memory, (H&P) CD8+ CD44hi CD62L− CCR7− effector memory. Data represent the mean ± SE of one of two independent experiment with 3 to 5 mice in each group. Student’s t test was performed to determine the statistical significance between BCG/IgG1 and BCG/α-IL-10R1 experimental groups. No statistical significant differences were found.