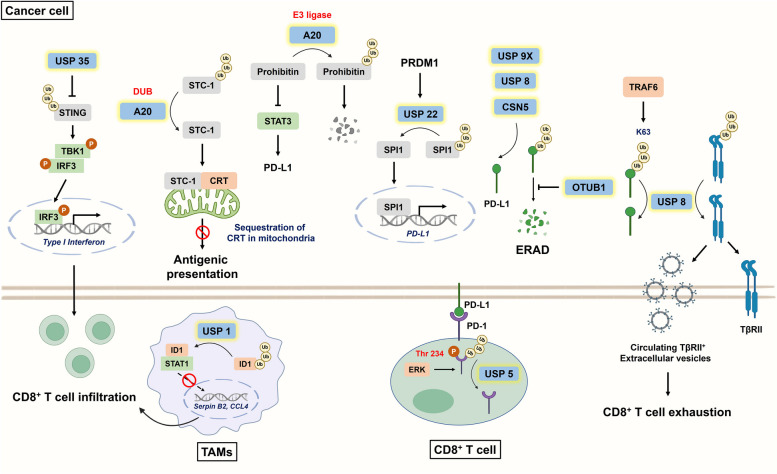
Fig. 3.
The involvement of DUBs in suppressing CD8+ T-cell infiltration and function. USP35 inhibits STING polyubiquitination and activation, ultimately downregulating IRF3-mediated type I interferon, which is important for CD8+ T-cell recruitment. Additionally, TAM-intrinsic USP1 deubiquitinates ID1 to prevent the nuclear translocation of STAT1 and the expression of CD8+ T-cell-recruiting factors (e.g., Serpin B2 and CCL4). A20 deubiquitinates and upregulates STC-1 to restrain the translocation of CRT from mitochondria to the plasma membrane, subsequently impeding antigenic presentation. With respect to CD8+ T-cell exhaustion, the PD-L1/PD-1 interaction has been extensively studied. Intriguingly, A20 upregulate PD-L1 via E3 ligase rather than deubiquitinating activity. Mechanistically, it ubiquitinates prohibitin but in turn induces STAT3/PD-L1 signaling