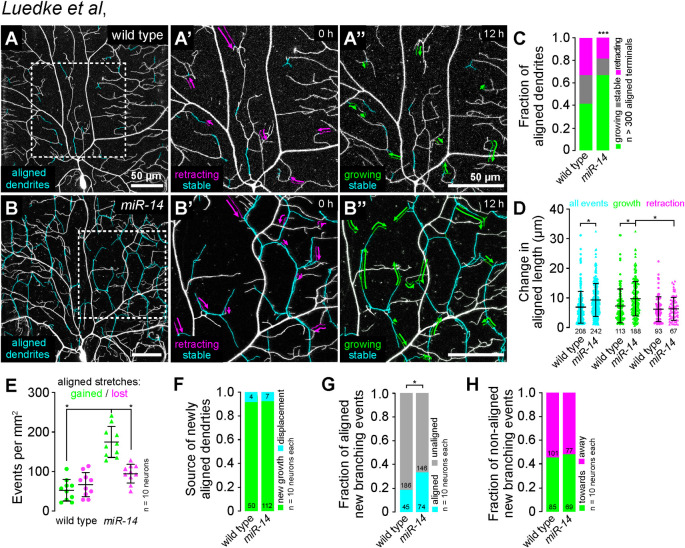
Fig 2. Time-lapse analysis of dendrite-epidermal junction interactions.
C4da neurons (ppk-CD4-tdTomato) were imaged over a 12 h time-lapse (108–120 h AEL) and dynamics were monitored for junction-aligned dendrites identified via co-localization with an epidermal junction marker (A58-GAL4, UAS-PLCδ-PH-GFP). Epidermal junction-aligned dendrites were pseudocolored cyan in the initial time point, and growth (green) and retraction (magenta) were pseudocolored in a composite of the two time points. Representative images are shown for (A) wild-type control and (B) miR-14 mutant larvae. (C) Stacked bar plot shows the fraction of junction-aligned dendrites that were growing, stable, or retracting over the time-lapse. (D) Extent of dynamics. Plot shows the change in length for each aligned dendrite measured (points) as well as mean and standard deviation. (E) Frequency of turnover in junctional alignment. Bars depict mean and standard deviation and data points represent the number of junctional-alignment events gained (green) or lost (magenta) during the time lapse for individual neurons, normalized to the area sampled. (F-H) Time-lapse imaging of new dendrite branch alignment relative to epidermal junctions. C4da neurons were imaged over a 24 h time lapse (96–120 h AEL) and the orientation of dendrite branch growth relative to epidermal junctions was monitored for each new dendrite branch. (F) Bars depict the proportion of newly aligned dendrite stretches (aligned to epidermal junctions at 120 h but not 96 h) that involve new dendrite growth (green) or reorientation of existing dendrites (cyan). Chi-square analysis revealed no significant difference between wild-type controls and miR-14 mutants. (G) A significantly larger proportion of new dendrite branches (present at 120 h but not 96 h) align along epidermal junctions in miR-14 mutants compared to wild-type controls. (H) Comparable portions of unaligned new dendrite branches in miR-14 mutants and wild-type controls orient towards (green) and away from (magenta) the nearest epidermal cell-cell interface. *P<0.05 compared to wild-type control unless otherwise indicated, Chi-square analysis (C, F-H), Kruskal-Wallis test with post-hoc Dunn’s test (D), or one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Sidak’s test (E).