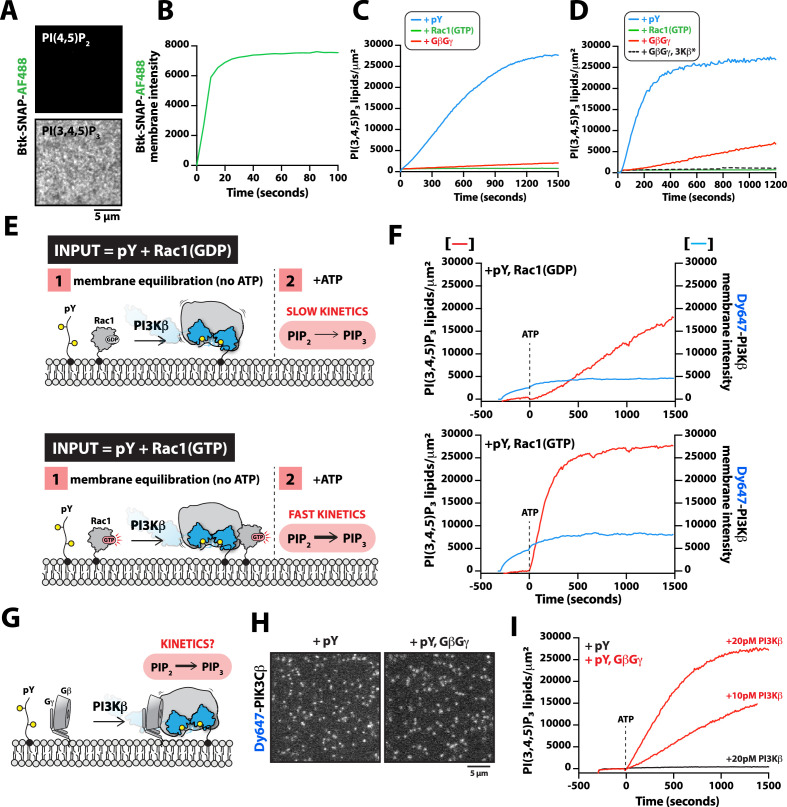
Figure 5. G-protein complexes (GβGγ) and Rac1(GTP) stimulate phosphoinositide 3-kinase beta (PI3Kβ) activity beyond enhancing localization on phosphorylated (pY) membranes.
(A) Representative TIRF-M images showing localization of 20 nM Btk-SNAP-AF488 on supported lipid bilayers (SLBs) containing either 2% PI(4,5)P2 or 2% PI(3,4,5)P3, plus 98% DOPC. (B) Bulk membrane recruitment kinetics of 20 nM Btk-SNAP-AF488 on an SLB measured by TIRF-M. (C–D) Kinetics of PI(3,4,5)P3 production measured in the presence of 10 nM Dy647-PI3Kβ and 1 mM ATP on SLBs with membrane anchored pY, Rac1(GTP), or GβGγ alone. Reactions in (C) were performed in the absence of PS lipids, while membranes in (D) contained 20% DOPS. (E) Cartoon schematic illustrating method for measuring Dy647-PI3Kβ activity in the presence of either pY/Rac1(GDP) or pY/Rac1(GTP). Phase 1 of the reconstitution involves membrane equilibration of Dy647-PI3Kβ in the absence of ATP. During phase 2, 1 mM ATP was added to stimulate lipid kinase activity of Dy647-PI3Kβ. (F) Dual color TIRF-M imaging showing 2 nM Dy647-PI3Kβ localization and catalysis measured in the presence of 20 nM Btk-SNAP-AF488. Dashed line represents the addition of 1 mM ATP to the reaction chamber. (G) Cartoon schematic showing experimental design for measuring synergistic binding and activation of Dy647-PI3Kβ in the presence of pY and GβGγ. (H) Representative single molecule TIRF-M images showing the localization of 20 pM Dy647-PI3Kβ in (G). (I) Kinetics of PI(3,4,5)P3 production monitored in the presence of 20 nM Btk-SNAP-AF488 and 10-20 pM Dy647-PI3Kβ. Membrane contained either pY or pY/GβGγ. (B, C, F, H, I) Membrane composition: 96% DOPC, 2% PI(4,5)P2, 2% MCC-PE. (D) Membrane composition: 76% DOPC, 20% DOPS, 2% PI(4,5)P2, 2% MCC-PE. All kinetic measurements of PI(3,4,5)P3 production were performed in the presence of 20 nM Btk-SNAP-AF488.