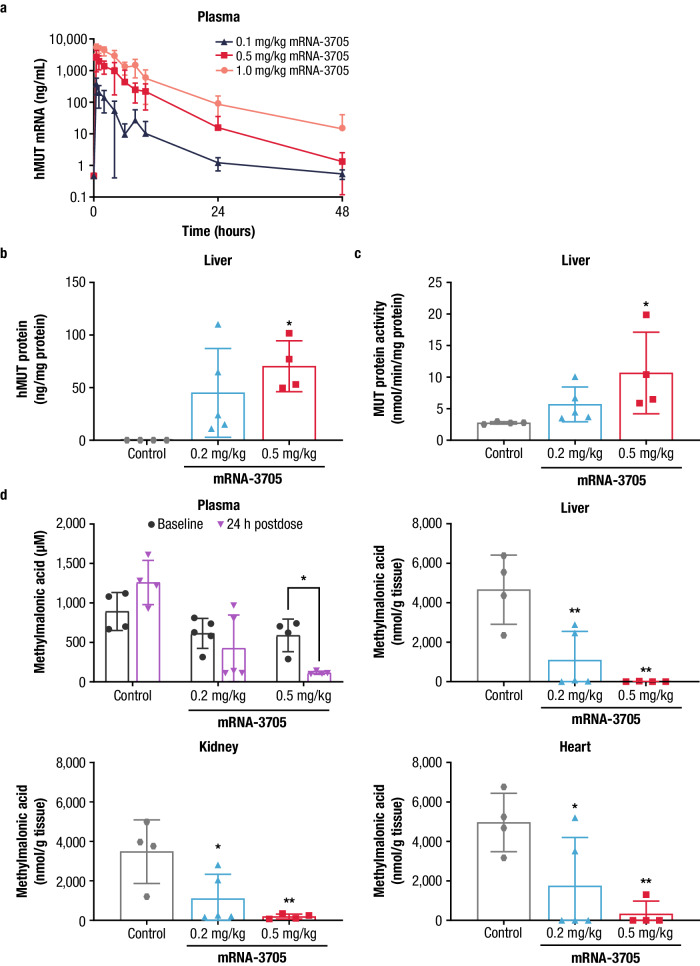
Fig. 3. Mean (±SD) concentrations of hMUT mRNA in CD1 mice and hMUT protein, enzyme activity, and methylmalonic acid levels in Mut−/−;TgINS-CBA-G715V hypomorphic mice treated with a single dose of mRNA-3705.
a CD1 mice received a single IV injection of mRNA-3705 (0.1, 0.5, or 1.0 mg/kg). Blood samples were collected on Day 1 at multiple time points up to 48 h postdose for hMUT mRNA quantitation via a bDNA method analysis (n = 6 mice/timepoint for all groups at 0.5, 1, 6, 8, 10, 24, and 48 hours postdose; and n = 12 mice/timepoint for all groups at 2 and 4 h postdose). b Mut−/−;TgINS-CBA-G715V hypomorphic mice received a single IV injection of either PBS (control) or mRNA-3705 (0.2 or 0.5 mg/kg). mRNA-encoded hMUT protein concentrations were quantified in the liver of mice receiving the indicated treatment 24 h postdose using a human-specific LC-MS/MS method (n = 4, 5, and 4 biologically independent mice per Control and 0.2 mg/kg and 0.5 mg/kg mRNA-3705, respectively). c A MUT activity assay that did not differentiate between human versus murine enzyme activity was used to assess total MUT enzyme activity (n = 4, 5, and 4 biologically independent mice per Control and 0.2 mg/kg and 0.5 mg/kg mRNA-3705, respectively). d Plasma methylmalonic acid levels were measured at baseline (Day -7) and 24 h postdose in mice receiving the indicated treatment (n = 4, 5, and 4 biologically independent mice per Control and 0.2 mg/kg and 0.5 mg/kg mRNA-3705, respectively). Liver, kidney, and heart methylmalonic acid levels were measured at 24 h postdose (n = 4, 5, and 4 biologically independent mice per Control and 0.2 mg/kg and 0.5 mg/kg mRNA-3705, respectively). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared to Mut−/−;TgINS-CBA-G715V PBS group by 1-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. ANOVA analysis of variance, bDNA branched DNA, hMUT human methylmalonyl-coenzyme A mutase, IV intravenous, LC-MS/MS liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, mRNA messenger RNA, PBS phosphate-buffered saline, SD standard deviation. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.