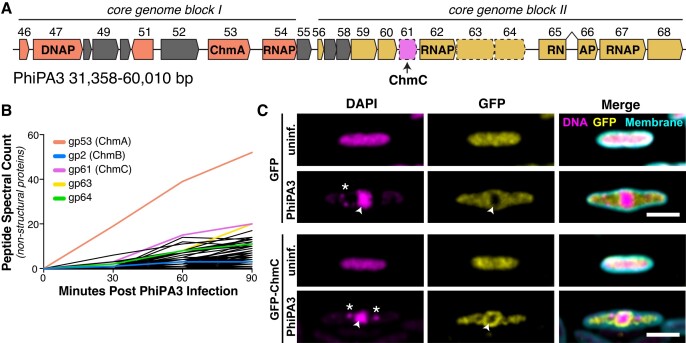
Figure 1.
PhiPA3 ChmC is associated with the phage nucleus. (A) Map of the PhiPA3 genome spanning jumbo phage conserved blocks I and II (3). Genes in conserved block I are colored salmon, and genes in conserved block II are colored goldenrod. Genes conserved with the closely related jumbo phage PhiKZ but not all jumbo phages are colored gray. gp47 is a putative DNA polymerase (DNAP), and gp53 is the major nuclear shell protein Chimallin (ChmA). Gp54, gp64, gp65-66 (interrupted by a self-splicing intron), and gp67 are subunits of the phage-encoded non-virion RNA polymerase (RNAP). Dotted outlines indicate three proteins (gp61/ChmC, gp63, and gp64) shown to be associated with the phage nuclear shell (15). (B) Mass spectrometry proteomics analysis of PhiPA3-infected P. aeruginosa, showing spectral counts of non-structural phage proteins. gp53 (ChmA), gp2 (ChmB), gp61 (ChmC), gp63 and gp64 are shown in colors and labeled. These data are from a single replicate from each time point. See Supplementary Tables S1 and S2 for full mass spectrometry results. (C) Localization of sfGFP (top) or sfGFP-fused PhiPA3 ChmC (bottom) in PhiPA3-infected P. aeruginosa cells at 75 min post infection. Magenta: DAPI nucleic acid dye; cyan: FM4-64 membrane dye; yellow: GFP. Arrowheads indicate phage nuclei, and asterisks indicate phage bouquets. Scale bar = 2 μm.