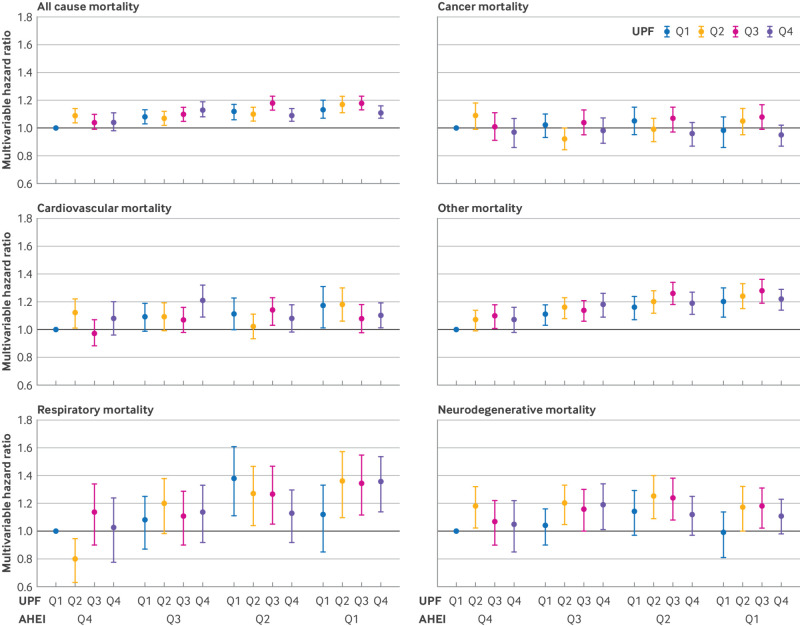
Fig 1.
Joint analysis for mortality according to quarters of ultra-processed food (UPF) consumption and quarters of Alternative Healthy Eating Index-2010 (AHEI) score. Alcohol was removed from calculation of AHEI score. Each participant was categorized according to their quarter of UPF intake and their quarter of AHEI score, resulting in 16 distinct groups. Using this combined variable as exposure, its association with mortality outcomes was assessed, with reference group being participants in highest quarter of AHEI score (Q4) and lowest quarter of UPF intake (Q1). Results were from multivariable Cox proportional hazards model stratified by age (months), questionnaire cycle (two year interval), and cohort and adjusted for total energy intake, race, marital status, physical activity, body mass index, smoking status and pack years, alcohol consumption, physical examination performed for screening purposes, and family history of diabetes mellitus, myocardial infarction, or cancer; for women, also menopausal status and hormone use. Markers denote point estimates of hazard ratios and error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals