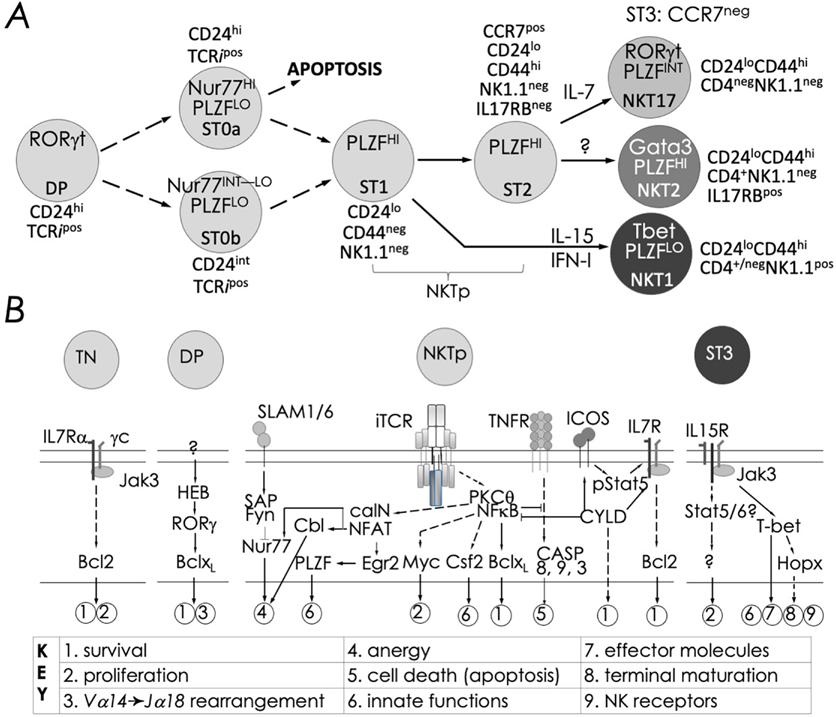
FIG. 7:
Schematic rendition of developmental stages and signaling events essential to NKT cell ontogeny: (A) Precursor ST0, immature ST1 & ST2, and mature ST3 represent distinct NKT cell developmental stages (ST) and NKT1, 2 and 17 are functional subsets. NKT cell ontogeny begins with the rearrangement of the TRAV11*02 to TRAJ18 TCR α-chain gene segments and proceeds after its interaction with the positively selecting CD1d-self lipid complex. Stage-specific NKT cell markers —e.g., CD24, CD44 and NK1.1—and subset-specific differentiation signals and transcription factors are indicated. Interleukin (IL)-7 and IL-15 are cytokines that mediate intercellular communication. (B) Thymocyte development to DP stage are essential for conventional CD4+ and CD8+ T as well as NKT cell development. Commitment to the NKT cell lineage occurs with the semi-invariant TCR expression at the DP stage under the influence of HEB (an E2A family transcription factor)- and RORγt. Positive selection at stage 0 induces the expression of PLZF, distinguishing NKT cells from other T lineages—e.g., CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Onward development requires signals relayed via the lymphocyte activation molecule family member (SLAMF)-SLAM-associated protein (SAP)-Fyn (a Src kinase) module, which tempers agonistic signals relayed through the NKT cell TCR. NKT cell TCR signals are processed by protein kinase C (PKC)-θ and relayed to CBM (CARMA1-Bcl10-MALT1) complex for integration by the transcription factor nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). Signals integrated by the SLAM-SAP-Fyn and the NKT cell TCR-PKC-θ-CBM-NF-κB modules culminate in Gata3 and Tbx21, encoding T-bet. The two transcription factors are essential for Il4 and Ifng transcription and lineage specific cytokine production. Calcineurin-NFAT-Egr2 and PKCθ-NF-κB signaling axes play essential roles in lineage proliferation (e.g., Myc), maintenance (e.g., Bcl-xL), and effector differentiation (e.g., Csf2), and maturation. Whilst the mechanism/s of subset differentiation are still debated, signals from IL-7 direct NKT17 cell differentiation and those from IL-15 and/or IFN-I (type I IFN) direct NKT1 cell differentiation. Transcription factors such as Egr-2, Ets-1, GATA3, Id2, Id3, MEF, Nur77, RORγt, and T-bet act at distinct stages shown to direct proper, functional NKT cell development. See text for details and references therein.