Extended Data Figure 2 |. Kinetics and sensitivity of the uLIPSTIC reaction.
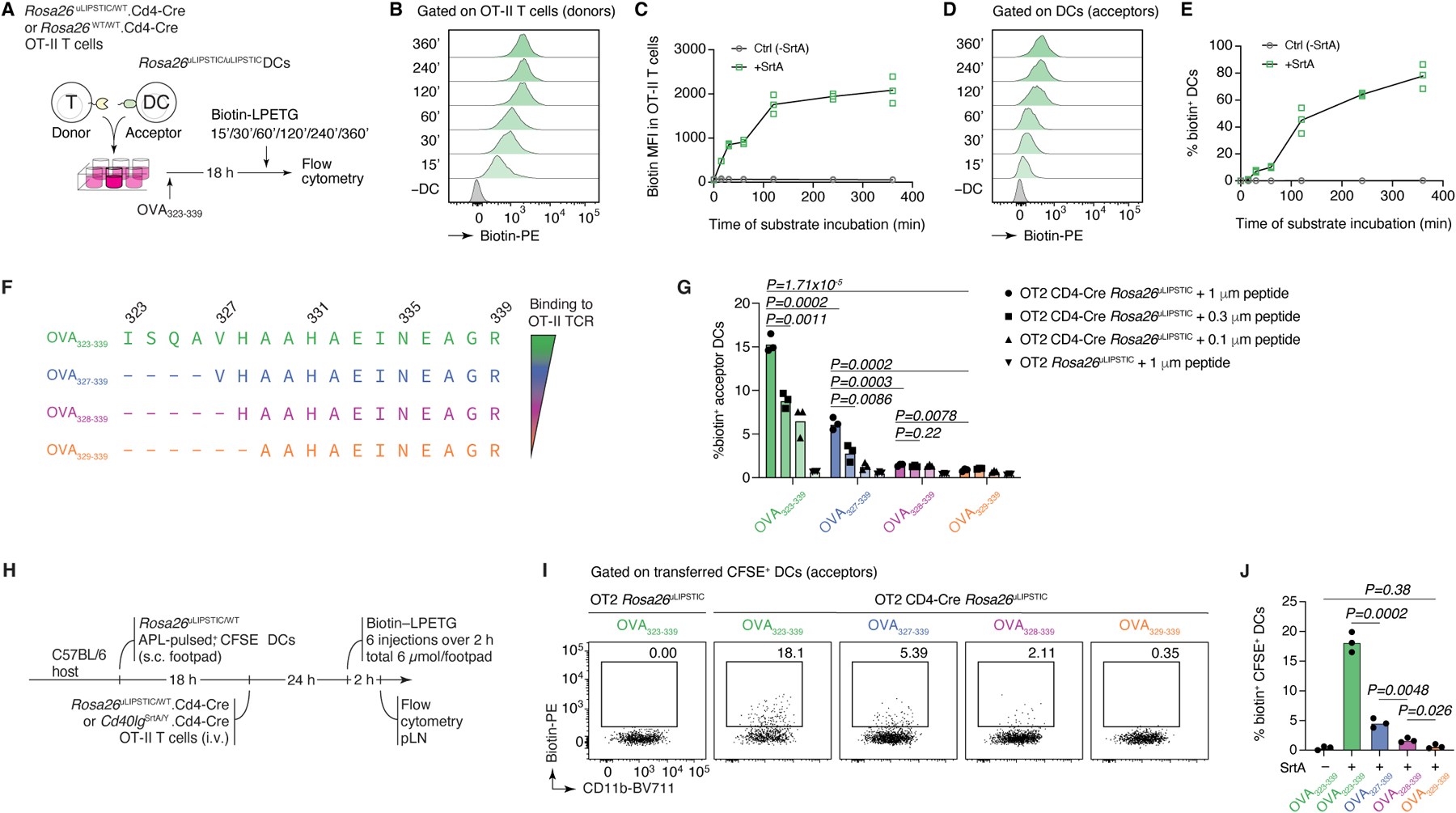
(A-E) Kinetics of the uLIPSTIC reaction. (A) Experimental setup for panels (B-E). OT-II CD4+ T cells from Rosa26uLIPSTIC/WT.CD4-Cre or Rosa26WT/WT.CD4-Cre control mice were co-incubated ex vivo with Rosa26uLIPSTIC/uLIPSTIC acceptor DCs in the presence of OVA323–339 cognate peptide. LIPSTIC substrate was added during the final minutes of incubation as indicated. (B,C) Efficiency of formation of the acyl intermediate (loading of LIPSTIC substrate onto SrtA) in OT-II SrtA+ donor T cells increases gradually with time. (D,E) Transfer of LIPSTIC substrate onto the surface of interacting acceptor DCs followed similar kinetics as acyl intermediate formation. (F-J) uLIPSTIC can resolve differences in peptide concentration and affinity both in vitro and in vivo. (F) Altered peptide ligands (APLs) of the OVA323–339 peptide, when complexed with MHC-II, display decreasing affinities for the OT-II TCR. (G) In vitro co-culture of Rosa26uLIPSTIC/WT.CD4-Cre OT-II T cells with Rosa26uLIPSTIC/uLIPSTIC DCs loaded with its APLs results in a reduction in LIPSTIC labeling that aligns with both the affinity of the peptide-MHCII complex to the OT-II TCR and the peptide concentration gradients. (H) Experimental layout for panels (I,J). (I) In vivo labeling of APL-pulsed DCs show decreased uLIPSTIC labeling in accordance with the affinity to the fixed OT-II TCR. Quantified in (J). Data for all plots are for three mice per condition from one experiment. P-values were calculated using two-tailed Student’s tests.
