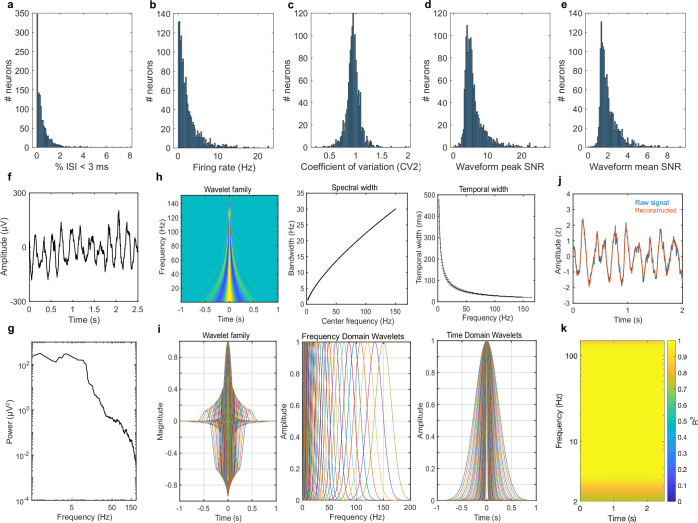
Extended Data Fig. 1. Spike-sorting quality metrics for all identified putative single units and wavelet characteristics.
(a-e) Spike-sorting quality metrics. (a) Proportion of inter-spike intervals (ISI) below 3 ms. (b) Average firing rate. (c) Coefficient-of-variation. (d) Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) for the peak of the mean waveform across all spikes as compared to the standard deviation of the background noise. (e) Mean SNR of the waveform. (f) Example raw LFP recorded in a hippocampal channel during the delay period of a single trial (time 0 denotes onset of the delay period). (g) Power-spectrum of LFP data shown in (f). (h,i) Wavelet characteristics for all 40 wavelets used. Left: Wavelet family. The upper panel shows the temporal outline and the magnitude of the real part for all wavelets smoothed across all frequencies. The maximal magnitude of each wavelet is scaled to 1. Warm colours denote positive, cold colours negative magnitude. The lower panel shows the real part of all wavelets plotted on top of each other. Centre: The upper panel shows the spectral bandwidth of each wavelet as a function of centre frequency. The lower panel plots the FFT-spectrum for each wavelet. Right: The upper panel shows the temporal width of all wavelets as a function of centre frequency. The horizontal lines indicate the spectral bandwidth for each wavelet. The lower panel contains the amplitude envelope for each wavelet as a function of time. (j) Example original and reconstructed signal after applying the continuous wavelet transform (see Methods). Small deviations from the original signal are due to the fact that signals at frequencies lower or higher than the edge frequencies of 2 and 150 Hz, respectively, were not represented by the wavelet transform but present in the original signal. (k) Assessment of the wavelet-based signal reconstruction. We computed linear models using the reconstructed signal as predictor for the original signal and extracted R-squared values as a function of time and frequency in each trial and channel. Values were averaged across all trials and all hippocampal channels. An R-squared values of close to 1 indicates almost perfect reconstruction of the original signal. As stated above, the slight drop in reconstruction quality at extreme frequencies is explained by the fact that signals at frequencies lower or higher than the edge frequencies, respectively, were not represented by the wavelet transform but present in the original signal.