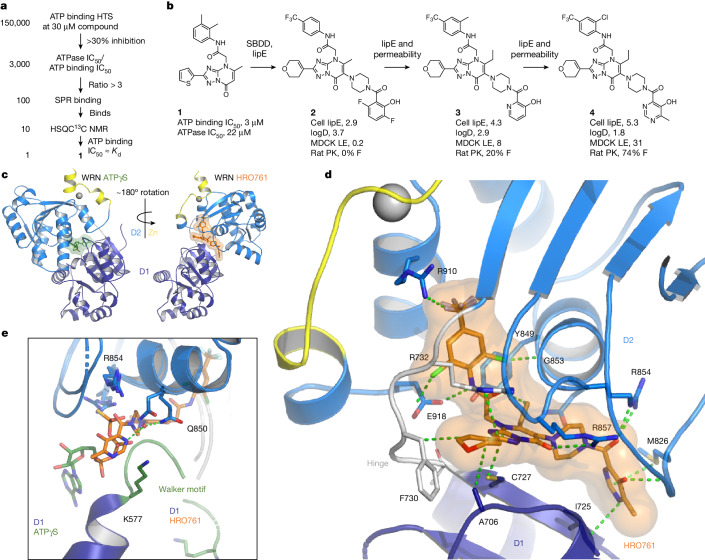
Fig. 1. Identification and structural basis of HRO761, an allosteric WRN inhibitor.
a, Screening funnel with hit count on the left and progression criteria on the right leading to the identification of hit 1. HTS, high-throughput screening; Kd, dissociation constant; NMR, nuclear magnetic resonance; SPR, surface plasmon resonance. b, The structure of hit 1 and medicinal chemistry optimization to clinical candidate 4, HRO761, with key profiling data of compounds 2–4 (cell lipE calculated from SW48 proliferation GI50 and the distribution coefficient between 1-octanol and water at pH 7.4 (logD), apparent permeability in low-efflux Madin–Darby canine kidney cells (MDCK LE Papp, 10−6 cm s−1), oral bioavailability (F) and structure based drug design (SBDD)). c, HRO761 is an allosteric inhibitor of the WRN helicase binding at the D1–D2 interface in a novel conformation involving a 180° rotation of the D1 and D2 domains relative to ATPγS-bound WRN (ligands are shown as sticks with transparent surface). d, Owing to the overlap with the D2 ATP half-site, the HRO761-binding site is unusually polar and rich in arginine residues. HRO761 makes extensive polar interactions and engages key residues of the flexible hinge (Thr728-Gly-Phe-Asp-Arg). e, Overlay of the D2 domains of ATPγS- and HRO761-bound WRN showing that HRO761 displaces the Walker motif (green) and its catalytic residue Lys577 through mimicry of the ATP γ-phosphate, including coordination of the hydrolytic water by Gln850.