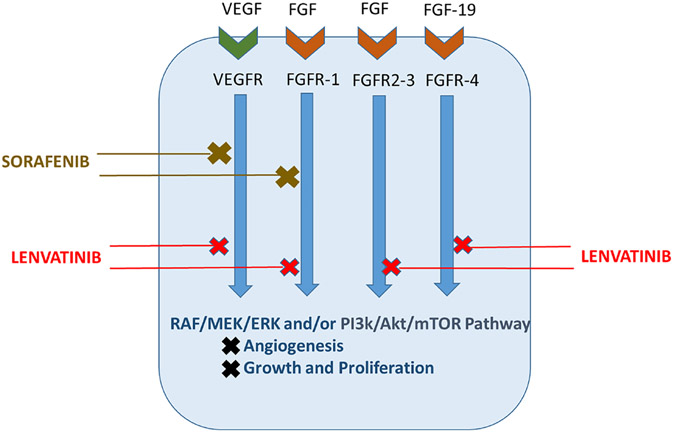
FIG. 1:
Mechanism of action for first-line HCC targeted molecular therapies. Current targeted therapies affect molecular pathways important in HCC development and metastatic ability. Shown are sorafenib, which competitively inhibits VEGFR and FGFR1 signaling at the receptor level and at their respective downstream signaling pathways, and lenvatinib, a preferred first-line targeted therapy due to its inhibition at multiple receptors and their associated downstream signal cascades. A primary target of lenvatinib is the receptor FGFR4, which has been shown to decrease the apoptotic ability of sorafenib if overexpressed.