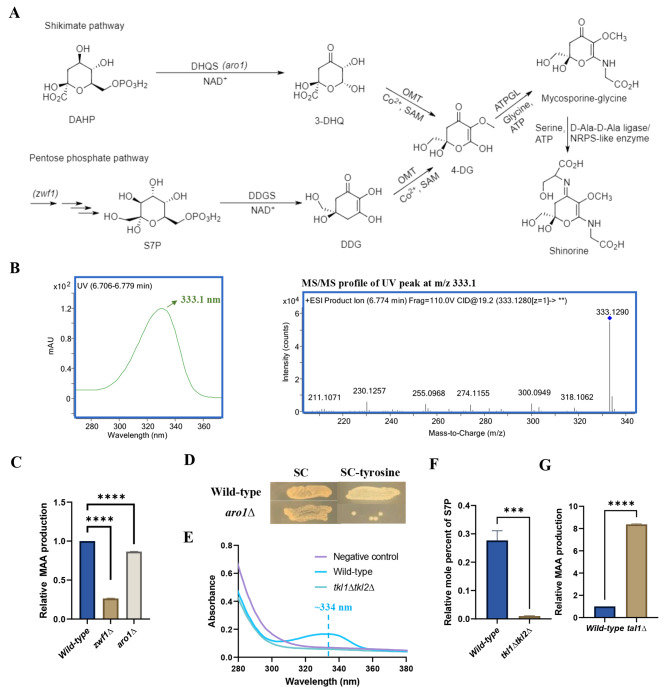
Fig. 1.
Recombinant production of MAAs in yeast requires the PPP but not the shikimate pathway. (A) Biosynthesis of MAA is proposed to occur from an intermediate derived from either the shikimate pathway or the pentose phosphate pathway. (DAHP = 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate, DHQS = 3-dehydroquinate synthase, 3-DHQ = 3-dehydroquinate, OMT = O-methyltransferase, DDG = demethyl 4-deoxygadusol, 4-DG = 4-deoxygadusol, ATPGL = ATP-grasp ligase, SAM = S-adenosyl methionine) (B) LC/MS analysis shows that the compound eluting at 6.733 min absorbs UV maximally at about 333 nm (left panel), and its corresponding MS/MS profile (right panel) agrees with the published MS/MS profile of shinorine. (C) Comparison of shinorine levels in the wild-type, zwf1∆ and aro1∆ strains. (D) The growth of the wild-type and aro1∆ cells on synthetic complete (SC) and tyrosine-dropout agar plates. (E) The UV absorption spectra of the tkl1∆tkl2∆ strain compared to the wild-type and negative control strains. The negative control strain refers to a strain which does not produce shinorine, as it only contains the first two genes (DDGS and OMT) of the shinorine biosynthetic pathway. (F) The relative mole percent of S7P in the wild-type compared to the tkl1∆tkl2∆ strain. (G) Comparison of shinorine production in the wild-type and ta11∆ strains. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments. Significance was determined using an unpaired t-test. *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001