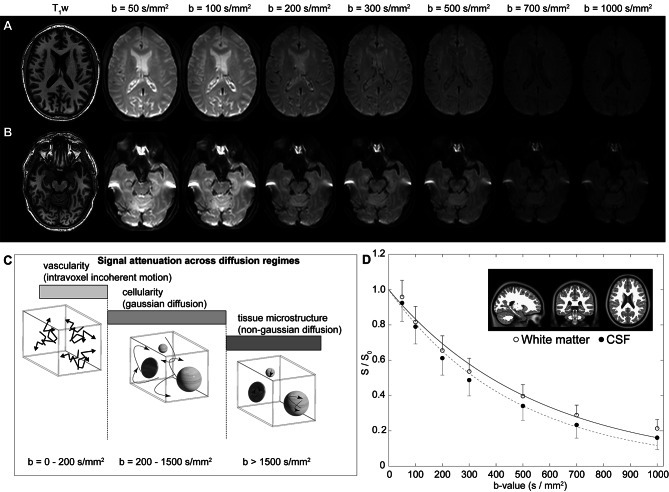
Fig. 1.
Multi-shell diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) using low-to-intermediate b-values. (A) Two slices at the level of the lateral ventricles (A) and suprasellar cistern (B) for a representative participant (age = 77 years; sex = male) are shown. (C) The approximate regime of physiological sensitivity for increasing b-values, whereby low b-values < 200 s/mm2 have known sensitivity to vascular structures and intravoxel incoherent motion, intermediate b-values of approxiamtely 200–1500 s/mm2 are sensitive to cellularity in the regime of gaussian diffusion, and high b-values above 1500 s/mm2 are most sensitive to non-gaussian diffusion and tissue microstructure assessments. (D) Example decay curves as a function of low-to-intermediate b-value in the transition range of intravoxel incoherent motion and gaussian diffusion demonstrate differences in cerebrospinal fluid and tissue. Error bars across the region shown in the insert are depicted as one-sided for clarity