FIGURE 1.
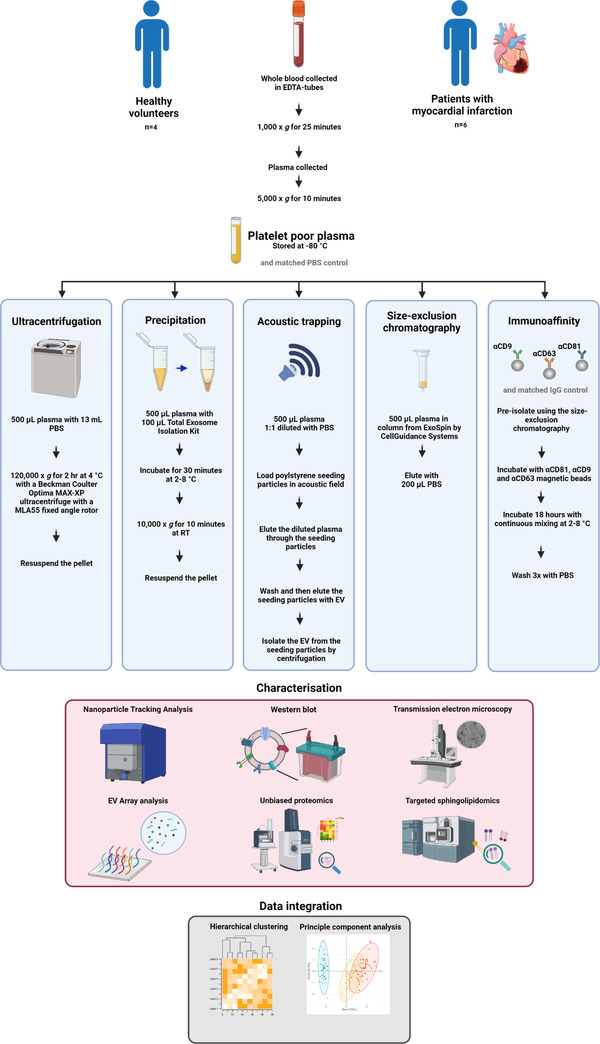
A methodological overview. Platelet‐poor plasma was obtained from healthy volunteers (n = 4) and patients presenting with myocardial infarction (MI) (n = 6) (and from the same patients 1‐month post‐MI) and plasma extracellular vesicles (EV) were isolated using five different methods: ultracentrifugation (UC), precipitation, acoustic trapping, size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and immunoaffinity capture with a matched vehicle phosphate buffered saline (PBS) or IgG control. The plasma EV were analysed using Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis, protein concentration, Western blot, transmission electron microscopy, a targeted EV‐protein array for EV‐markers CD9, CD63, CD81, ALIX, TSG101, flotillin, Annexin V, and 18 other cell associated markers, untargeted proteomics (LC‐MS/MS) and targeted sphingolipidomics (LC‐MS/MS). The data were analyzed in isolation and following integrated hierarchical clustering and principal component analysis. Room temperature (RT).
