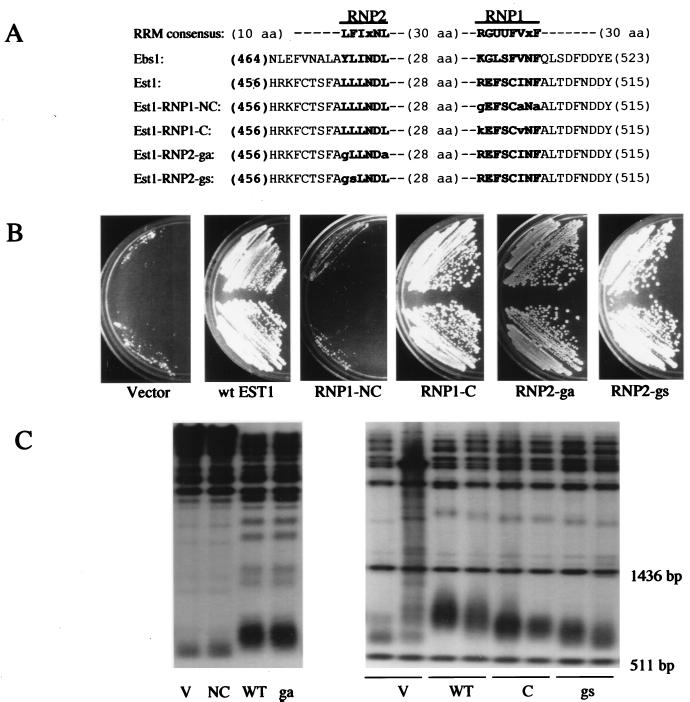
FIG. 5.
Phenotypes caused by altering the RRM region of Est1. (A) The RRM consensus sequence (1, 17) is compared to RRM-like regions in Ebs1 and Est1. The most highly conserved regions (RNP1 and RNP2) are shown in bold lettering. U, hydrophobic amino acid (aa). The amino acid changes made in the four est1 mutants are indicated by lowercase letters. To the right of RNP1 in Est1 is the sequence FNDDY; F is F511, and the first D is D513. These amino acids are altered in two previously characterized alleles of est1 (43) (see the Discussion). (B) A presenescent est1Δ strain (about 35 generations removed from the original spore clone) was transformed with plasmids based on pJZ-3HA-EST1 harboring the empty vector, wild-type (wt) EST1, or the NC, C, ga, or gs mutant allele of EST1. Two independent colonies from each transformation were streaked on YEPD plates and photographed after 60 h of growth. (C) Genomic DNA was extracted from each transformant, digested with XhoI (left panel) or PstI (right panel), and fractionated by agarose gel electrophoresis. After Southern blotting, telomeric DNA was detected with 32P-labeled oligo TELPG. V, transformants containing an empty vector; WT, wild type. In the right panel, the two sharp bands just below and above the fuzzy telomere bands are molecular size markers of 511 and 1,436 bp, respectively (see Materials and Methods).