FIGURE 6.
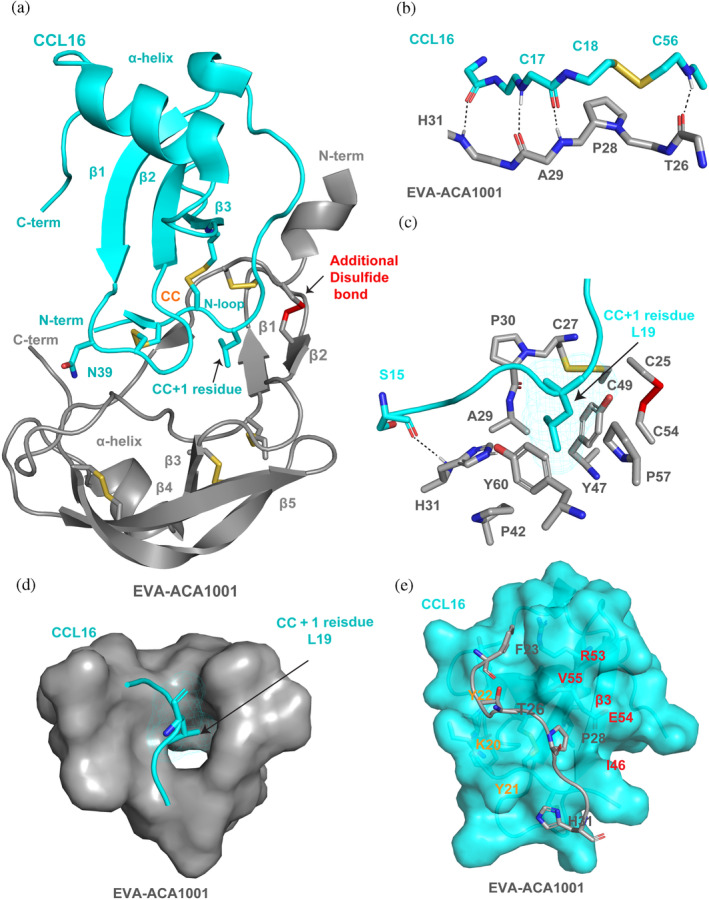
Structural basis of broad‐spectrum chemokine binding by EVA‐ACA1001. (a) Structure of EVA‐ACA1001 in complex with CCL16. EVA‐ACA1001 is shown as gray ribbons; disulfides conserved with subclass A1 evasins are shown as yellow sticks; the unique disulfide in subclass A3 evasins is shown as red sticks. CCL16 is shown as cyan ribbons; conserved disulfides are shown as yellow sticks. Selected residues (the CC + 1 residue, Leu19 and Asn39) are also shown as sticks. (b) Backbone‐backbone hydrogen bond interactions between the β1 region of EVA‐ACA1001 and the CC motif (and adjacent residues) of CCL16. (c) Interaction of the EVA‐ACA1001 hydrophobic pocket (colored gray, blue, red, and yellow, by atom type) with the CCL16 CC + 1 residue, Leu19 (cyan). (d) Surface representation showing the EVA‐ACA1001 binding pocket (gray surface) holding the CCL16 CC + 1 residue, Leu19 (sticks). (e) The EVA‐ACA1001 extended region at the junction between the N‐terminus and the core (gray) forms interactions with a shallow groove formed by the N‐loop (Lys20‐Tyr22) and the β3‐strand (Ile46‐Arg53) of CCL16, shown as a space‐filling model in cyan; important residues of the N‐loop (orange) and the β3‐strand (red) are labeled.
