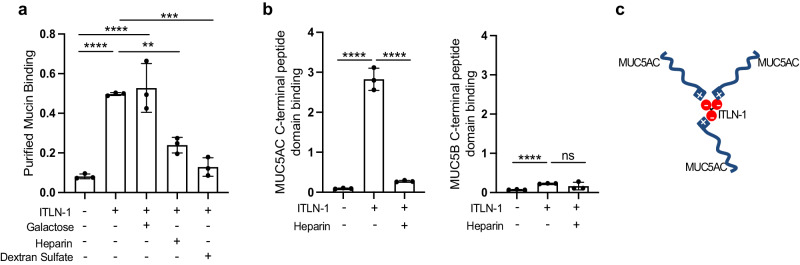
Fig. 3. ITLN-1 binds to purified airway mucins and to the C-terminal domain of MUC5AC.
a Bar graphs measuring binding of recombinant flag-tagged ITLN-1 protein, and the effect of co-incubation with galactose, heparin, or dextran sulfate, to purified human airway mucins (isolated and pooled from n = 5 participants). Data represent mean values ± SD; one way ANOVA with multiple comparisons **p = 0.0032, ***p = 0.0002, and ****p < 0.0001. b Binding assays measuring the ability of ITLN-1 protein, or co-incubated ITLN-1 + heparin, to bind to immobilized C-terminal peptides of MUC5AC (left) or MUC5B (right). Data representative of n = 3 independent experiments and bar plots represent mean values ± SD; Two-sided t test ****p < 0.0001, ns = not significant. c Illustration of the potential mechanism by which an ITLN-1 protein trimer could interact with the C-terminal domain of MUC5AC mucin molecules via electrostatic interactions. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.