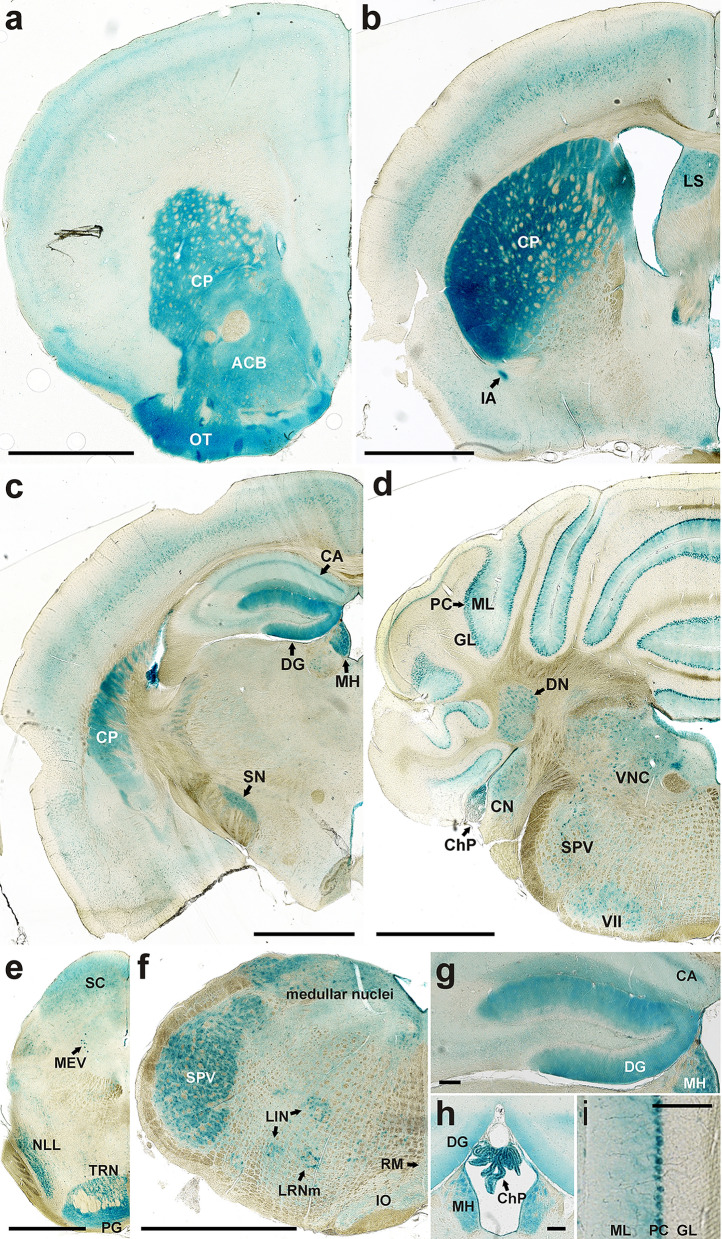
Figure 2.
LacZ histochemistry detects differential Lrba expression levels in multiple neuronal cell populations. Frontal sections of the septo-striatal region (a), the septo-diencephalic region (b), the caudal diencephalon (c), the rostral cerebellum (d), the caudal mesencephalon (e) and the medulla oblongata (f) are shown in rostro-caudal order. The dentate gyrus (g), the 3rd ventricle with the chorioid plexus (h), and the cerebellar cortex (i) are shown at higher magnifications. Abbreviations of LacZ-positive features: ACB nucleus accumbens, CA1 hippocampus (cornu ammonis), ChP chorioid plexus, CN cochlear nuclei, CP caudato-putamen, DG dentate gyrus, DN dentate nucleus, GL granular layer, IA intercalated amygdalar nucleus, IO inferior olivary complex, LIN linear nucleus of the medulla, LRNm lateral reticular nucleus magnocellular part, LS lateral septal nucleus, MEV midbrain trigeminal nucleus, MH medial habenula, ML molecular layer, NLL nucleus of the lateral lemniscus, OT olfactory tubercle, PC Purkinje cells, PG pontine gray, RM nucleus raphe magnus, SC superior colliculus, SN substantia nigra, SPV spinal nucleus of the trigeminal, TRN trigeminal reticular nucleus, VII facial motor nucleus, VNC vestibular nuclei. Scale bars: 1 mm in (a–f), 100 µm in (g–i).