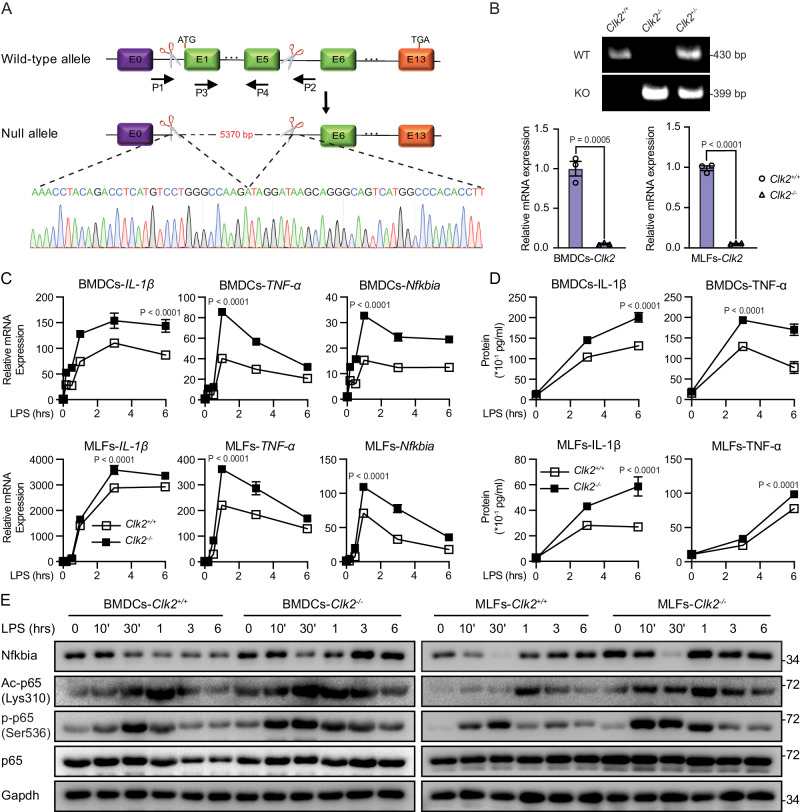
Fig. 2. Clk2 deficiency enhances the NF-κB-mediated inflammatory response.
A The targeting strategy for the deletion of exons 1–5 of Clk2 and the DNA sequence of the Clk2−/− genome. B Generation and identification of Clk2-deficient mice at the genomic and mRNA levels (n = 3). The PCR products of Clk2WT and Clk2KO. C Real-time PCR analysis of IL-1β, TNF-α and Nfkbia mRNA levels in Clk2+/+ and Clk2−/− BMDCs and MLFs stimulated with LPS (200 ng/ml) for the indicated times (n = 3). D ELISA analysis of IL-1β and TNF-α protein levels in Clk2+/+ and Clk2−/− BMDCs and MLFs stimulated with LPS for the indicated times (n = 3). E Western blot analysis of Nfkbia, Ac-p65K310, p-p65S536, p65 and Gapdh in Clk2+/+ and Clk2−/− BMDCs and MLFs stimulated with LPS for the indicated times. The data are representative of three independent experiments. The data are presented as the means ± SEMs (n = 3 for B–D). Statistical significance was analyzed by two-tailed Student’s t test (B) or two-tailed ANOVA (C, D) (***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001). Source data (A–E) are provided as a Source Data file.