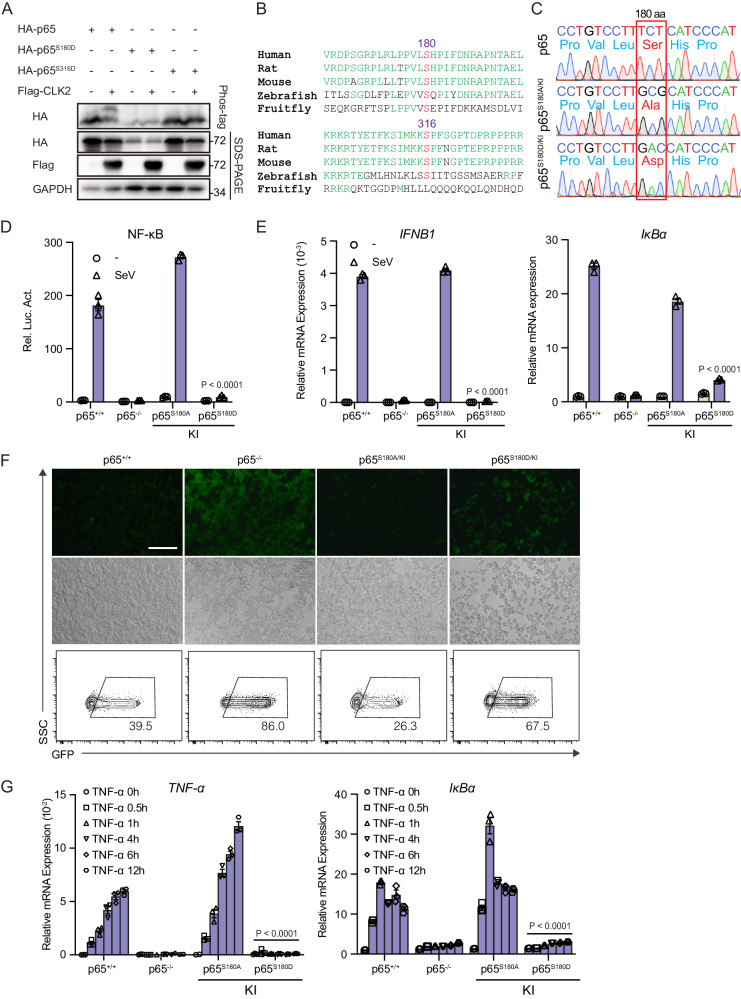
Fig. 5. The phosphorylation of p65 at Ser180 by CLK2 inhibits the transcriptional ability of activated NF-κB.
A Phos-tag SDS‒PAGE analysis of the phosphorylation of the p65 residues 180 and 316 in the presence or absence of CLK2 in HEK293T cells. The upper shifted band represents the phosphorylated p65 protein. B Conserved site analysis of the p65 residues 180 and 316 from fruit flies to humans. C Identification of p65 knock-in cell lines by sequencing. D Luciferase reporter experiments analyzing NF-κB activity in the indicated cells infected with SeV for 24 h (n = 3). E Real-time PCR analysis of IFNB1 and IκBα mRNA levels in the indicated cells infected with SeV for 12 h (n = 3). F The effects of p65 mutants on VSV-GFP infection for 12 h before phase contrast and fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometric analysis in the indicated cells. The scale bar is 250 µm. G Real-time PCR analysis of IκBα and TNF-α mRNA levels in cells exposed to 20 ng/ml TNF-α for 0 h. 0.5, 1, 4, 6, and 12 h (n = 3). The data are representative of three independent experiments. The data are presented as the means ± SEMs. Statistical significance was analyzed by two-tailed ANOVA (D, E, G) (****p < 0.0001). Source data (A–G) are provided as a Source Data file.