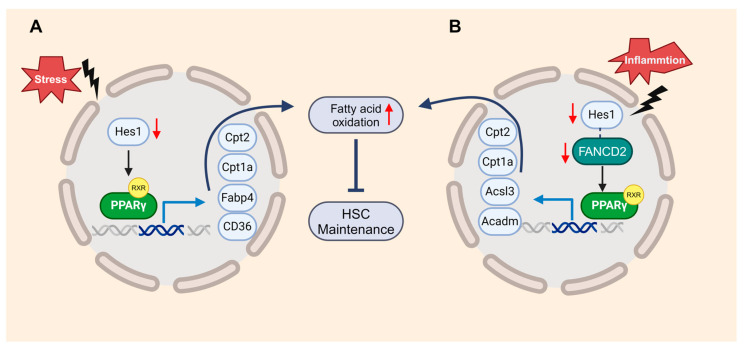
Figure 4.
FANCD2 and HES1 act in concert to suppress inflammation-induced PPARγ to prevent HSC exhaustion through restricting fatty acid oxidation (FAO). (A). Loss of Hes1 deregulates genes in PPARγ signaling and FAO, thereby augment FAO in HSPCs. (B). A novel FANCD2/HES1/PPARγ axis constitutes a key component of immunemetabolic regulation, connection inflammation, cellular metabolism and HSC function.