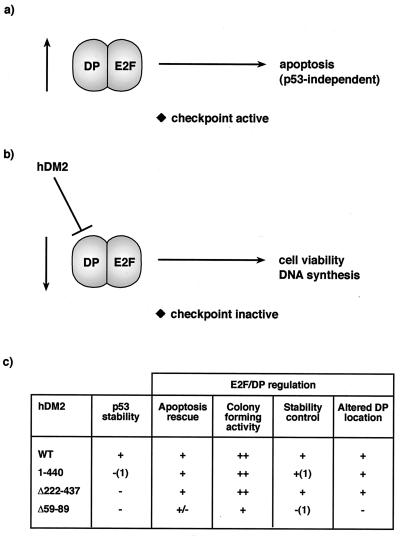
FIG. 8.
Model for regulation of E2F by hDM2. (a and b) It is envisaged that inappropriately high levels of E2F-DP activity cause the activation of a checkpoint pathway of control which thereafter leads to apoptosis (a). Since hDM2 can influence apoptosis by causing a reduction in E2F and DP subunit levels (b), it is suggested that this process may allow hDM2 to modulate checkpoint activity, limit apoptosis, and thereby facilitate cell cycle progression. The data suggest that the DP subunit is instrumental in enabling hDM2 to regulate E2F-dependent apoptosis. (c) Summary of the effects of hDM2 and mutant derivatives on E2F-DP regulation. (1), data not shown.