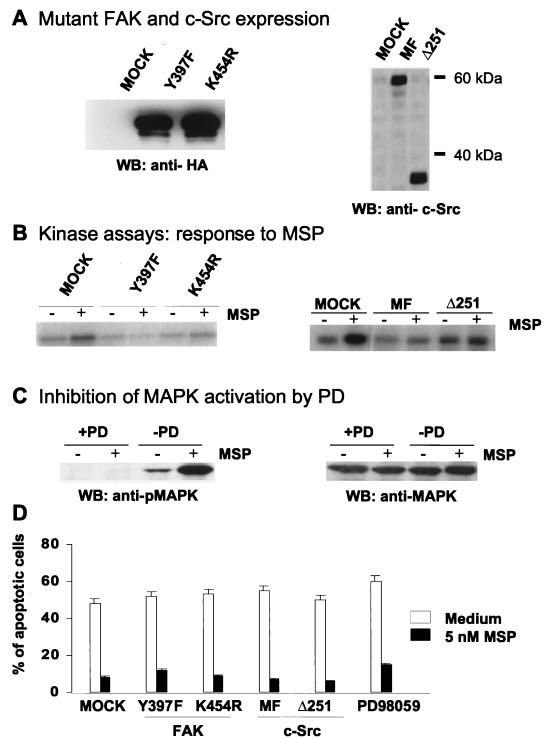
FIG. 3.
Inhibition of MSP-induced FAK, c-Src, or MAPK activation does not prevent the antianoikis effect of MSP. (A) RE7 cells were transiently transfected with dominant-negative FAK Y397F or K454R or c-Src MF or Δ251 or empty vector (mock). Lysates (15 μl/lane) from transfected and MACS4-selected cells were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting with anti-HA antibodies for detection of FAK expression (left) and with anti-c-Src antibodies for detection of c-Src expression (right) (B) A suspension of transiently transfected RE7 cells (2 × 106/ml) was stimulated with 5 nM MSP for 10 min. FAK and c-Src kinases were then immunoprecipitated from cell lysates with anti-FAK or anti-c-Src antibodies. The kinase activities of FAK and c-Src were measured with [32P]ATP as the capacity of the FAK IP to autophosphorylate FAK (left) or the c-Src IP to phosphorylate enolase (right), detected by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. (C) A suspension of RE7 cells was pretreated with 50 μM MEK inhibitor PD98059 for 15 min, and then the cells were stimulated with 5 nM MSP for an additional 15 min. Activation of MAPK was determined by Western blotting with anti-phosphoMAPK (pMAPK) (left) or anti-MAPK (right) after SDS-PAGE of total cell lysates. (D) Anoikis was induced in mutant FAK or c-Src-transfected RE7 cells as described in the legend to Fig. 1. After overnight incubation in medium with or without 5 nM MSP, the apoptotic cells were quantified by TUNEL staining. Each experimental point represents the mean percentage (+ standard error of the mean) of apoptotic cells for three independent experiments.