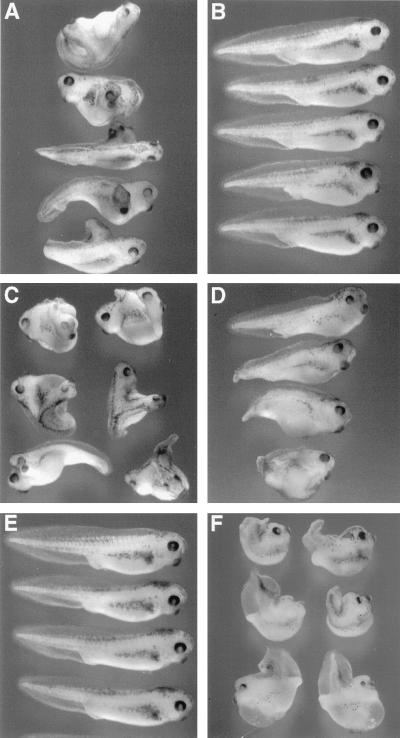
FIG. 6.
The requirement for the DIX domains of Xdsh and XARP in signal transduction. Four- to eight-cell embryos were injected into a single ventrovegetal blastomere with 1 ng of HA-Xdsh mRNA (A) or HA-Xdsh-BC mRNA (B), 1 pg of Xwnt8 mRNA (C), or 1 pg of Xwnt8 mRNA with 2 ng of XARP-C mRNA (D). Secondary axes and other morphological abnormalities were scored when uninjected sibling embryos (E) reached stages 36 to 39. The results show that the DIX domain of Xdsh is required for its functional activity (A and B), whereas the DIX domain of XARP blocks Wnt signaling (C to E). Dorsal injections of XARP-C mRNA (2 ng) do not eliminate the primary axis but suppress morphogenetic movements in the trunk-tail region (F).