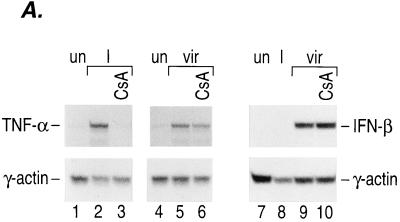
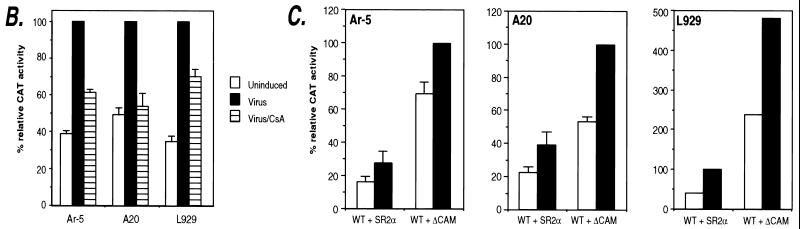
FIG. 2.
Calcineurin is involved in virus-inducible TNF-α gene induction. (A) Induction of TNF-α mRNA by ionophore and virus in Ar-5 T cells. An autoradiogram of an RNase protection assay mapping TNF-α and γ-actin mRNAs is shown. Ar-5 cells were stimulated with ionomycin (I) for 30 min or with Sendai virus (vir) for 2 h in the presence or absence of CsA. The γ-actin probe was made to have a specific activity that was one-fifth the specific activity of the mouse TNF-α probe. (B) CsA inhibits virus induction of TNF-α CAT reporter activity. Ar-5 T cells, A20 B cells, or L929 fibroblasts were transfected with the −200 TNF-α–CAT reporter gene. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were mock induced (Uninduced) or stimulated with Sendai virus (Virus) in the presence or absence of CsA as indicated in the figure. CAT assays were performed and quantified as described in the legend to Fig. 1. The figure shows the results of three independent experiments. (C) Calcineurin augments virus induction of TNF-α. Ar-5 T cells, A20 B cells, or L929 fibroblasts were transfected with the −200 TNF-α–CAT reporter gene and a plasmid that constitutively expresses the catalytic subunit of calcineurin (ΔCAM) or a control plasmid (SR2α) as indicated in the figure. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were either mock induced (Uninduced) or stimulated with Sendai virus (Virus) as described for panel B. CAT assays were performed and quantified as described in the legend to Fig. 1. The figure shows the results of three independent experiments for Ar-5 and A20 cells and a representative experiment for L929 cells.