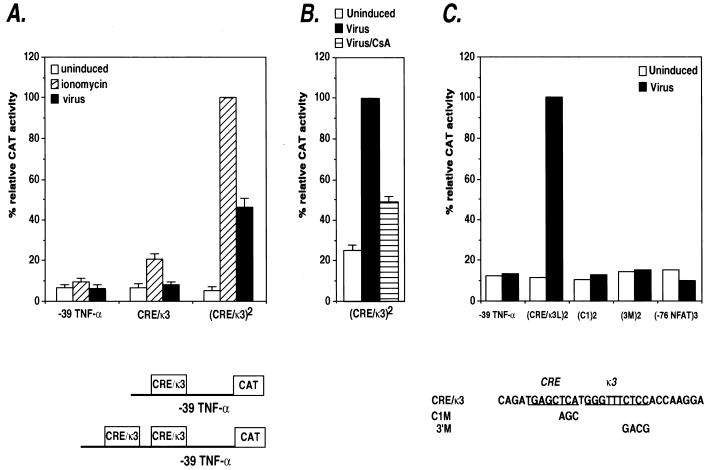
FIG. 4.
Inducer-specific regulation of the CRE/κ3 composite element by ionophore and virus. (A) Activation of synthetic TNF-α promoters containing the CRE/κ3 multimers by ionomycin or virus in Ar-5 T cells. Ar-5 cells were transfected with the truncated −39 TNF-α–CAT construct containing either one or two copies of the κ3(L) site. Twenty-four hours later, the cells were mock stimulated (uninduced) or stimulated with ionomycin (ionomycin) or Sendai virus (virus). Within the individual experiments displayed, the results were normalized to the induced level (100%) of the wild-type (CRE/κ3)2 multimer construct and then averaged and plotted in the displayed histogram. CAT assays were performed and quantified as described in the legend to Fig. 1. The figure shows the results of three independent experiments. (B) CsA inhibits virus activation of the CRE/κ3 site. Ar-5 cells were transfected with the κ3(L)2 synthetic promoter construct, stimulated with virus in the presence or absence of CsA, and analyzed and quantified as described in the legend to Fig. 1. The figure shows the results of three independent experiments. (C) Activation of synthetic TNF-α promoters containing CRE/κ3 or −76-NFAT multimers in Ar-5 T cells. Ar-5 cells were transfected with the truncated −39 TNF-α–CAT construct containing either two copies of the wild-type CRE/κ3 site or two copies of the CRE/κ3 site containing the 3′ mutation or the C1 mutation or with three copies of the −76-NFAT site as indicated in the figure. Twenty-four hours later, the cells were mock stimulated (Uninduced) or stimulated with Sendai virus (Virus) as indicated. The figure shows a representative experiment. The results were normalized to the induced level (100%) of the wild-type (CRE/κ3)2 multimer construct and then averaged and plotted in the displayed histogram.