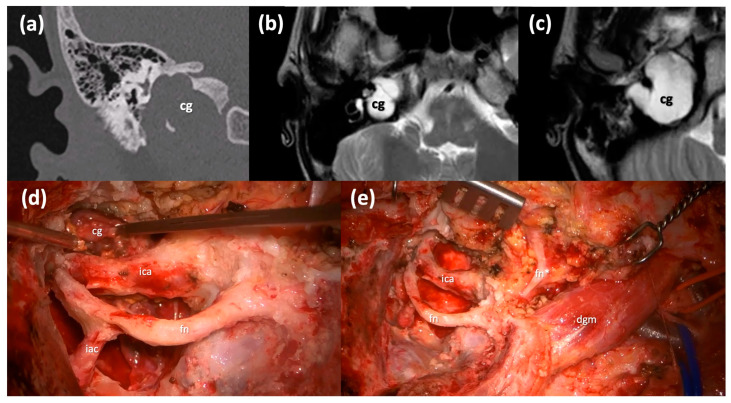
Figure 4.
Type B infratemporal fossa approach combined with a transotic approach. (a) Coronal CT scan of a massive right Type C PACG. (b,c) Axial T2-weighted MRI sections of the same PACG showing its hyperintense signal and its relationship with the IAC, the ICA and the clivus. (d) Surgical step: the facial nerve has been completely skeletonized from the IAC to the stylomastoid foramen and it is left in a bridge-like fashion over the surgical field; careful maneuvers are employed to dethatch the PACG from the horizontal segment of the ICA. (e) Surgical step: final surgical field where the PACG has been completely removed. cg, cholesterol granuloma; ica, internal carotid artery; fn, mastoid segment of the facial nerve; iac, internal auditory canal; fn*, intraparotid facial nerve; dgm, digastric muscle.