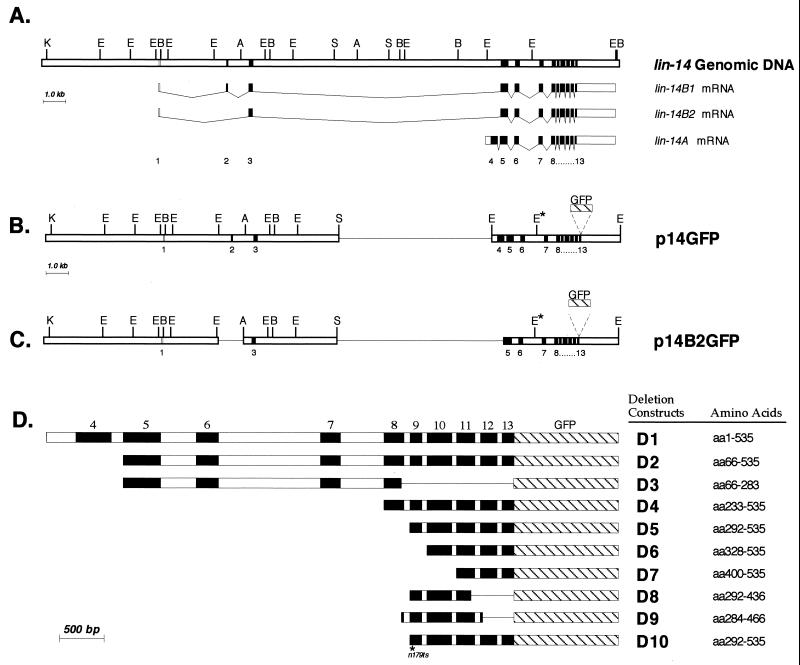
FIG. 1.
Genomic organization of wild-type lin-14 and lin-14 deletion constructs. (A) lin-14 intron-exon structure of the three identified lin-14 transcripts, lin-14B1, lin-14B2, and lin-14A (adapted from reference 28). Restriction enzyme map and intron-exon spacing are drawn to scale. Open box in exon 4 indicates that the 5′ end of the exon 4 open reading frame is undetermined. A, AgeI; B, BglII; E, EcoRI; K, KpnI; S, SalI. (B and C) LIN-14 deletion-GFP fusion constructs p14GFP and p14B2GFP. A single line represents a region that is deleted. E∗, EcoRI site that was eliminated (see Materials and Methods). (D) Truncated lin-14 constructs expressed from the col-10 promoter. col-10 promoter sequences and 3′UTR sequence of lin-14 are not shown. Open boxes indicate introns and filled boxes indicate exons. GFP sequence is represented by the hatched box (artificial introns in GFP are not shown). Amino acids are numbered according to Wightman et al. (28). D10 contains the lin-14(n179ts) mutation (R303G in exon 9; B. Reinhart and G. Ruvkun, personal communication; see Materials and Methods).