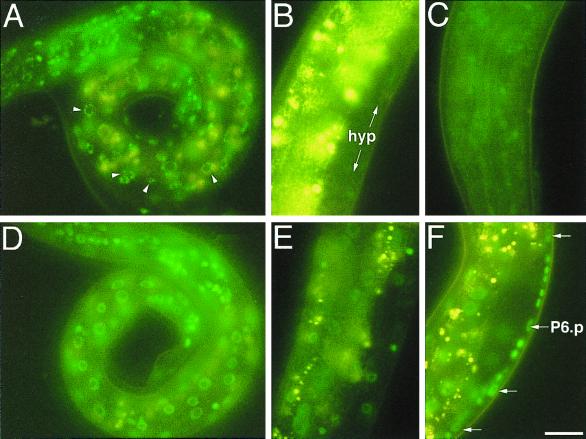
FIG. 2.
lin-4-dependent down regulation of LIN-14::GFP from maEx166. (A) Newly hatched transgenic L1 larva carrying maEx166, which was generated by injection of p14GFP (Fig. 1). High levels of green LIN-14::GFP fluorescence is evident in hypodermal cells, muscle cells, intestinal cells, and neurons. Arrowheads point to nuclei that show punctuate LIN-14::GFP fluorescence typical of this construct. The yellow fluorescence seen in these images is due to the autofluorescence from the intestine. (B) LIN-14::GFP expression in maEx166 animals becomes virtually undetectable in hypodermal cells (hyp) by the L3 stage. Yellow signal is (non-GFP) intestinal autofluorescence. (C) In maEx166 animals, LIN-14::GFP expression in the head neurons remains detectable in some L3 animals. (D) lin-4(e912); maEx166 L1 larvae display fluorescence levels approximately equal to that of lin-4(+); maEx166 L1 larvae. (E) At the L3 stage, high levels of LIN-14::GFP expression persists in hypodermal cells and in intestinal cells of lin4(e912); maEx166 L3 larvae. (F) Expression of LIN-14::GFP in VPC (Pn.p) cells is easily detectable in this lin-4(e912); maEx166 L2 larva [but is undetectable in similarly staged lin-4(+); maEx166 L2 larvae; not shown]. Animals in B, E, and F are all oriented anterior down and ventral side to the right. Bar, 3 μm.