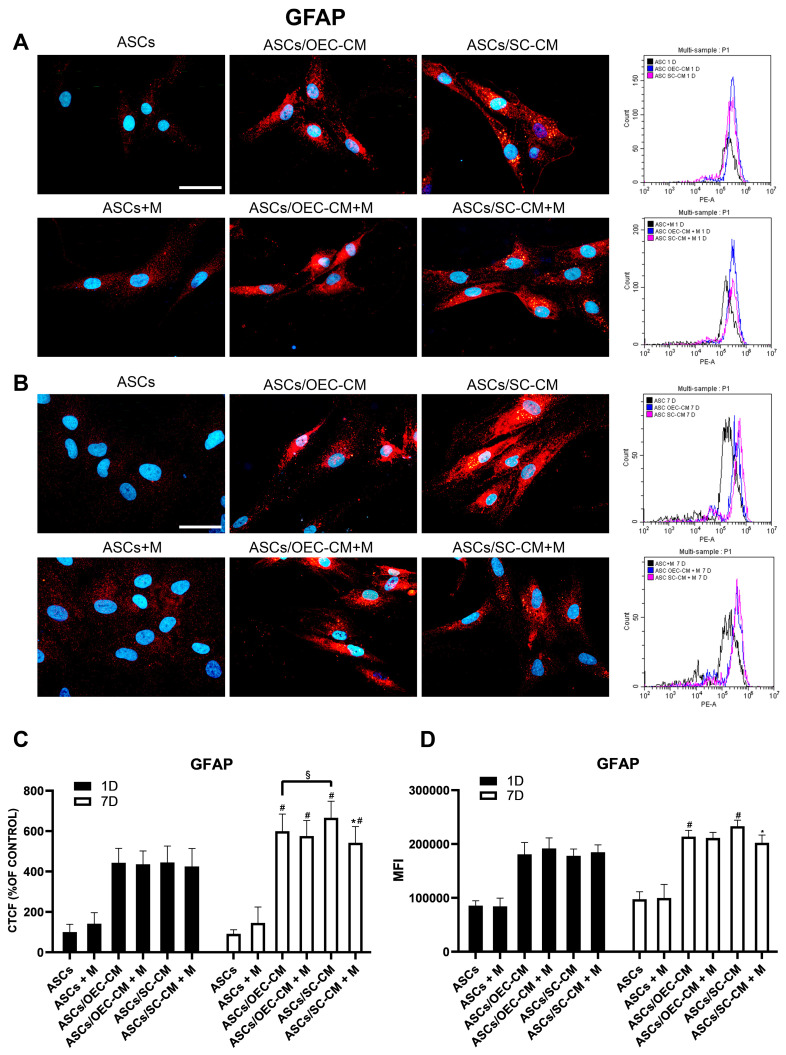
Figure 6.
GFAP expression in ASC cultures. The different conditions were investigated by immunocytochemistry and flow cytometry after 1 (A) and 7 (B) days of culture. In each row, microphotographs are followed by flow cytometry histograms (fourth column) in the same conditions. Quantitative immunofluorescence data (ImageJ) and flow cytometry mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) are also reported in panels (C,D), respectively. A weak basal expression of GFAP is detectable when ASCs are grown in their basal medium, on both day 1 and 7, regardless of the presence of melatonin (first column). A significant increase is observed on both day 1 and 7 when glial CM were used (second and third column). The addition of melatonin to glial CM did not affect GFAP expression on day 1, whereas it attenuates CM-induced increases on day 7, especially in combination with SC-CM. Blue fluorescence counterstaining indicates cell nuclei. Scale bars: 50 µm. Quantitative data reported in the histograms (panels C,D) confirm the GFAP expression modifications above described. Each plot in panel (C) summarizes a total of 60 measurements. * p < 0.05 melatonin presence vs. corresponding melatonin absence; # p < 0.05 day 7 vs. day 1; § p < 0.05 OEC-CM vs. SC-CM with or without melatonin.