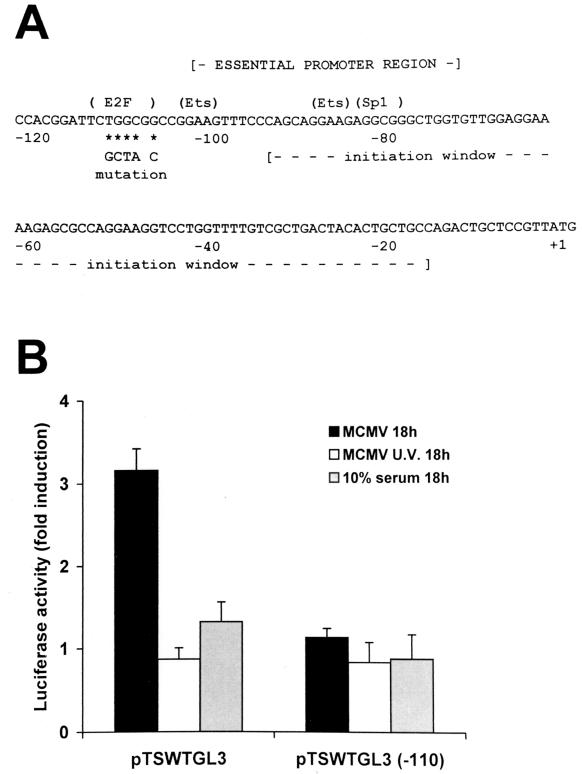
FIG. 4.
E2F binding site of the TS promoter required for MCMV-mediated transactivation. (A) Sequence of the mouse TS promoter region. The locations of the essential promoter region, the transcriptional initiation window, the potential binding sites for E2F, Ets, and SP1, and the AUG translational start codon are indicated. The nucleotide changes made in the E2F element in the −110 TS promoter mutation are shown under the wild-type sequence. (B) Effect of inactivation of the E2F element. NIH 3T3 cells were transiently transfected with 2 μg of the indicator construct pTSWTGL3, which contains the wild-type TS promoter region, or pTSWTGL3(−110), which contains the E2F mutation, and 10 μg of carrier DNA (pBluescript SK). After 18 h, cells were washed and growth arrested in 0.5% calf serum for 48 h. Thereafter, transfectants were infected with MCMV or UV-irradiated MCMV, mock infected, or serum stimulated to reenter the cell cycle. Total cytoplasmic extracts were isolated at 18 h after virus infection or serum stimulation and assayed for luciferase activity. Reporter gene activity was normalized to the amount of plasmid DNA introduced into recipient cells by DNA dot blot analysis. The resulting luciferase activity is expressed as fold induction relative to basal levels measured in cells transfected with pTSWTGL3 or pTSWTGL3(−110) and then mock infected, which was set at 1. The data shown are the averages of three experiments ± the standard errors of the means (error bars).