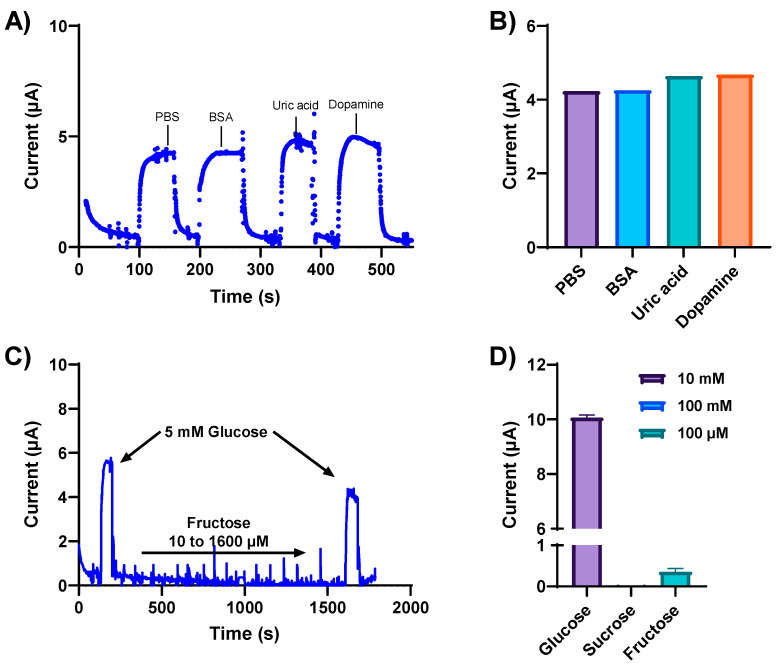
Figure 4.
Specificity and selectivity of the glucose sensor were determined in the presence of various interfering electroactive constituents. (A) Chronoamperometric response obtained at 0.2 V from the NH2-Fc-functionalized glucose biosensor for 5 mM glucose in PBS spiked with the electroactive interferants BSA, uric acid, and dopamine. (B) Box plot representation of current response obtained with 2.5 mg/mL BSA, 1 mM uric acid, and 10 μM dopamine spiked separately in a solution containing 5 mM glucose in PBS. (C) Amperometry response of the NH2-Fc-functionalized glucose sensor with varying concentrations of fructose demonstrating sensor specificity. (D) Plot showing the specificity of the developed glucose biosensor for glucose detection compared with other saccharides, sucrose and fructose. Data represented here are from n = 2 replicates.