Figure 3.
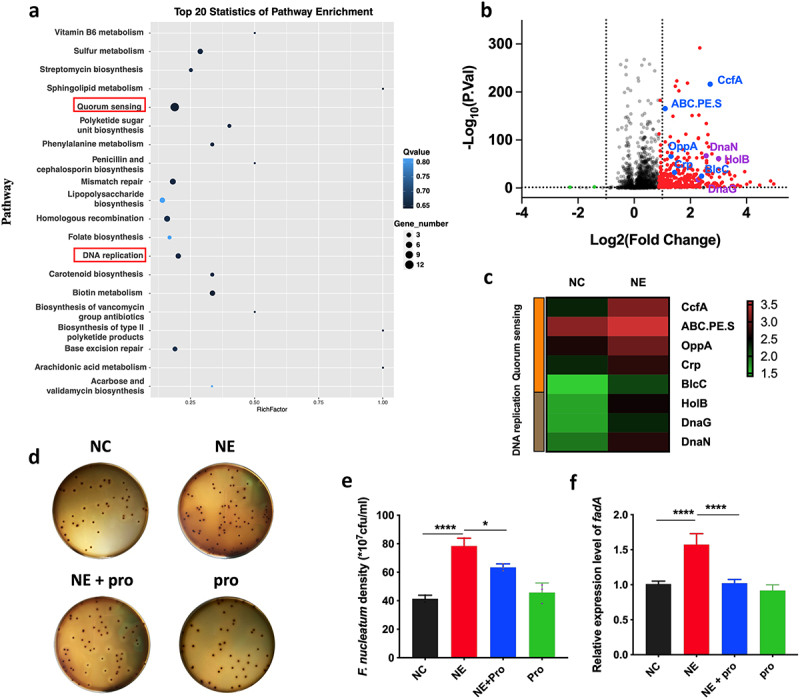
NE promoted the virulence and proliferation of F. nucleatum with upregulation of QS system (a) F. nucleatum was treated with NE for 24 hours followed by subjection to RNA-Seq. KEGG analysis of pathway enrichment showed the induction of QS after NE treatment. (b) volcano plot of the transcriptome in NE group versus NC group. QS associated genes (ccfA, ABC.PE.S, oppA, crp, blcC) and DNA replication associated genes (holB, dnaG, dnaN) were labelled. (c) Heatmap of differentially regulated genes associated with QS and DNA replication. (d) Representative images of the colony formation of F. nucleatum subjected to NE and propranolol treatments. (e) statistics of F. nucleatum density based on the colonies in (d). (f) qRT-PCR data showed that fadA expression was increased significantly with treatment of NE, and decreased by propranolol. All experiments were repeated three times, and one-way analysis of variance was used.
*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. F. nucleatum, Fusobacterium nucleatum; QS, quorum sensing; NC, Negative control; NE, norepinephrine; pro, propranolol, NE inhibitor.
